Fis Regulates Type III Secretion System by Influencing the Transcription of exsA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain PA14
- PMID: 28469612
- PMCID: PMC5395579
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00669
Fis Regulates Type III Secretion System by Influencing the Transcription of exsA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain PA14
Abstract
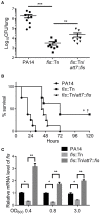
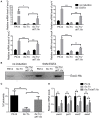
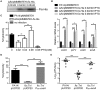
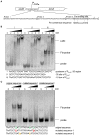
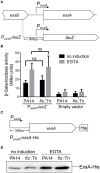
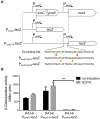
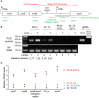
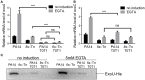
Fis is a versatile DNA binding protein in bacteria. It has been demonstrated in multiple bacteria that Fis plays crucial roles in regulating bacterial virulence factors and optimizing bacterial adaptation to various environments. However, the role of Fis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence as well as gene regulation remains largely unknown. Here, we found that Fis was required for the virulence of P. aeruginosa in a murine acute pneumonia model. Transcriptome analysis revealed that expression of T3SS genes, including master regulator ExsA, was defective in a fis::Tn mutant. We further demonstrate that the continuous transcription of exsC, exsE, exsB, and exsA driven by the exsC promoter was required for the activation of T3SS. Fis was found to specifically bind to the exsB-exsA intergenic region and plays an essential role in the transcription elongation from exsB to exsA. Therefore, we found a novel role of Fis in the regulation of exsA expression.
Keywords: Fis; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; bacterial virulence; exsA transcription; type III secretion system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
H-NS Family Members MvaT and MvaU Regulate the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion System.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jun 21;201(14):e00054-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00054-19. Print 2019 Jul 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30782629 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the nucleoid-associated protein Fis (PA4853) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2020 May 1;76(Pt 5):209-215. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X20005427. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2020. PMID: 32356522 Free PMC article.
-
Vfr Directly Activates exsA Transcription To Regulate Expression of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion System.J Bacteriol. 2016 Apr 14;198(9):1442-50. doi: 10.1128/JB.00049-16. Print 2016 May. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 26929300 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical characterization of a regulatory cascade controlling transcription of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion system.J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 2;282(9):6136-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611664200. Epub 2006 Dec 29. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17197437
-
Fitting Pieces into the Puzzle of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion System Gene Expression.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jun 10;201(13):e00209-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00209-19. Print 2019 Jul 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31010903 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fis Contributes to Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Ciprofloxacin by Regulating Pyocin Synthesis.J Bacteriol. 2020 May 11;202(11):e00064-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00064-20. Print 2020 May 11. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32205461 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory protein SrpA controls phage infection and core cellular processes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Nat Commun. 2018 May 10;9(1):1846. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04232-6. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29748556 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion system by a novel calcium-responsive signaling pathway.iScience. 2024 Apr 9;27(5):109690. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109690. eCollection 2024 May 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38660402 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel PhoP-PhoQ Regulated Genes That Contribute to Polymyxin B Tolerance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microorganisms. 2021 Feb 9;9(2):344. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9020344. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33572426 Free PMC article.
-
HigB Reciprocally Controls Biofilm Formation and the Expression of Type III Secretion System Genes through Influencing the Intracellular c-di-GMP Level in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Oct 24;10(11):424. doi: 10.3390/toxins10110424. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30355991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Audic S., Claverie J. M. (1997). The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res. 7, 986–995. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

