Neural stem cells over-expressing brain-derived neurotrophic factor promote neuronal survival and cytoskeletal protein expression in traumatic brain injury sites
- PMID: 28469658
- PMCID: PMC5399721
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.202947
Neural stem cells over-expressing brain-derived neurotrophic factor promote neuronal survival and cytoskeletal protein expression in traumatic brain injury sites
Abstract
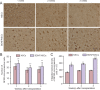
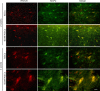
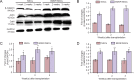
Cytoskeletal proteins are involved in neuronal survival. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor can increase expression of cytoskeletal proteins during regeneration after axonal injury. However, the effect of neural stem cells genetically modified by brain-derived neurotrophic factor transplantation on neuronal survival in the injury site still remains unclear. To examine this, we established a rat model of traumatic brain injury by controlled cortical impact. At 72 hours after injury, 2 × 107 cells/mL neural stem cells overexpressing brain-derived neurotrophic factor or naive neural stem cells (3 mL) were injected into the injured cortex. At 1-3 weeks after transplantation, expression of neurofilament 200, microtubule-associated protein 2, actin, calmodulin, and beta-catenin were remarkably increased in the injury sites. These findings confirm that brain-derived neurotrophic factor-transfected neural stem cells contribute to neuronal survival, growth, and differentiation in the injury sites. The underlying mechanisms may be associated with increased expression of cytoskeletal proteins and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Keywords: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; calmodulin; Wnt/β-catenin; cytoskeleton; differentiation; microtubule-associated proteins; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration; neural stem cells; neurofilament; transfect; traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Promotes Growth of Neurons and Neural Stem Cells Possibly by Triggering the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/ AKT/Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β/β-catenin Pathway.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017;16(7):828-836. doi: 10.2174/1871527316666170518170422. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017. PMID: 28524001
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulates proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells, possibly by triggering the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.J Neurosci Res. 2013 Jan;91(1):30-41. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23138. Epub 2012 Oct 1. J Neurosci Res. 2013. PMID: 23023811
-
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Increases Synaptic Protein Levels via the MAPK/Erk Signaling Pathway and Nrf2/Trx Axis Following the Transplantation of Neural Stem Cells in a Rat Model of Traumatic Brain Injury.Neurochem Res. 2017 Nov;42(11):3073-3083. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2340-7. Epub 2017 Aug 5. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28780733
-
Roles of neural stem cells in the repair of peripheral nerve injury.Neural Regen Res. 2017 Dec;12(12):2106-2112. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.221171. Neural Regen Res. 2017. PMID: 29323053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A growing field: The regulation of axonal regeneration by Wnt signaling.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Jan;13(1):43-52. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.224359. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 29451203 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regenerative Effects of Heme Oxygenase Metabolites on Neuroinflammatory Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 25;20(1):78. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010078. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30585210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Theaflavin attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by abolishing miRNA‑128‑3p‑mediated Nrf2 inhibition and reducing oxidative stress.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Dec;20(6):4893-4904. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10755. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31638230 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in genetically modified neural stem cell therapy for central nervous system injury and neurological diseases.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Dec 18;15(1):482. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-04089-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39696712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promising therapeutic effects of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (HF-rTMS) in addressing autism spectrum disorder induced by valproic acid.Front Neurosci. 2024 Aug 22;18:1385488. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1385488. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39238929 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation in the Evolution of Motor Function in Stroke and Trauma Patients: Treatment and Potential Biomarkers.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Oct 25;45(11):8552-8585. doi: 10.3390/cimb45110539. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37998716 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bonnet C, Boucher D, Lazereg S, Pedrotti B, Islam K, Denoulet P, Larcher JC. Differential binding regulation of microtubule-associated proteins MAP1A, MAP1B, and MAP2 by tubulin polyglutamylation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:12839–12848. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

