Toxic effects of seu are different from those of other staphylococcal enterotoxins
- PMID: 28469769
- PMCID: PMC5411912
Toxic effects of seu are different from those of other staphylococcal enterotoxins
Abstract
Background/purpose: Staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) are soluble extracellular proteins excreted by Staphylococcal bacterial strains, sharing similar structures and virulence. More than 20 genotypes of SEs have been identified, but the toxicity of some new SEs is still unclear.
Methods: In this study, we assessed the toxicity effects of six recombinant SEs (rSEA, rSEO, rSEG, rSEK, rSEU and rSEQ) on Balb/c mice by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)-based methods and enzyme activity detection.
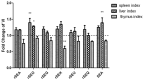
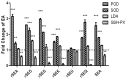
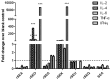
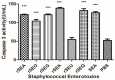
Results: Except rSEU, the other five SEs resulted in systemic inflammatory responses with a significant increase of spleen and liver index and decrease of thymus index. SEs enhanced the enzyme activities of liver POD, T-SOD, LDH but reduced the activity of liver GSH-PX. The transcription levels of five cytokines were all down-regulated by rSEA, rSEG and rSEQ at a dose of 20 ng/g, which was coincided with the results of Caspase 3 level. The transcription and expression of IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-6, and TNF-α involved in inflammatory response were significantly up-regulated by rSEs at a low dose (20 ng/mL) except rSEU in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: Our results reveals that the rSEA, rSEO, rSEG, rSEK, and rSEQ have cytotoxicity and superantigenicity for Balb/c mice except the rSEU enterotoxin.
Keywords: Staphylococcal enterotoxin; cytokine; cytotoxicity; enzyme activity; genotype.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




References
-
- Chen TR, Hsiao MH, Chiou CS, Tsen HY. Development and use of PCR primers for the investigation of C1, C2 and C3 enterotoxin types of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from food-borne outbreaks. Int J Food Microbiol. 2001;71:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Bachert C, Gevaert P, van Cauwenberge P. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins: a key in airway disease? Allergy. 2002;57:480–487. - PubMed
-
- Bohach GA, Fast DJ, Nelson RD, Schlievert PM. Staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins involved in toxic shock syndrome and related illnesses. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1990;17:251–272. - PubMed
-
- Johler S, Tichaczek-Dischinger PS, Rau J, Sihto HM, Lehner A, Adam M, Stephan R. Outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning due to SEA-producing staphylococcus aureus. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2013;10:777–781. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
