MLN4924 protects against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the early inflammatory process
- PMID: 28469786
- PMCID: PMC5411929
MLN4924 protects against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the early inflammatory process
Abstract
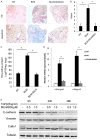
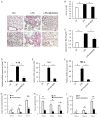
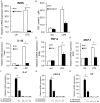
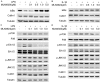
Pulmonary fibrosis is a complex pathological process characterized by massive destruction of the structure of lung tissues and aggravated pulmonary function impairment. The underlying mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis are incompletely understood and therefore limited treatment options are available currently. Here, we report that MLN4924, an NEDD8 activation enzyme (NAE) activity-inhibiting molecule, blocks the maintenance and progression of established pulmonary fibrosis. We found that MLN4924 acts against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis mainly at the early inflammatory stage. Pharmacologically targeting the neddylation of Cullin-Ring E3 ligase (CRL) by MLN4924, significantly abrogated NF-κB responses, suppressed MAPK activity, and reduced secretion of TNF-α-elicited pro-inflammatory cytokines and MCP1-induced chemokines. MLN4924 inhibited pro-inflammatory responses while maintaining or increasing the production of the anti-inflammatory mediators such as anti-inflammatory interleukins (ILs) following bleomycin administration, which is closely correlated to its blocking NF-κB-mediated signaling. Consistently, our studies identified MLN4924 as a promising therapeutic drug for pulmonary fibrosis and suggested a potential role of MLN4924 that fine tunes the MAPK signaling pathway controlling the inflammatory reactions at the early stages of pulmonary fibrosis. In addition, our findings may broaden the potential practical application of MLN4924 as an effective therapeutic strategy against other inflammation-associated diseases.
Keywords: MLN4924; bleomycin; inflammation; pulmonary fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of neddylation plays protective role in lipopolysaccharide-induced kidney damage through CRL-mediated NF-κB pathways.Am J Transl Res. 2019 May 15;11(5):2830-2842. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31217857 Free PMC article.
-
MLN4924 protects against interleukin-17A-induced pulmonary inflammation by disrupting ACT1-mediated signaling.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019 Jun 1;316(6):L1070-L1080. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00349.2018. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30892082
-
Neddylation-Independent Activities of MLN4924.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1217:363-372. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1025-0_21. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31898238 Review.
-
Neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 suppresses growth and migration of human gastric cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 11;6:24218. doi: 10.1038/srep24218. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27063292 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting DCN1-UBC12 Protein-Protein Interaction for Regulation of Neddylation Pathway.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1217:349-362. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1025-0_20. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31898237 Review.
Cited by
-
Kelch-like protein 42 is a profibrotic ubiquitin E3 ligase involved in systemic sclerosis.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 27;295(13):4171-4180. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC119.012066. Epub 2020 Feb 17. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32071084 Free PMC article.
-
Protein neddylation and its role in health and diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Apr 5;9(1):85. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01800-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38575611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin-proteasome signaling in lung injury.Transl Res. 2018 Aug;198:29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29752900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A first-in-human, phase 1 study of the NEDD8 activating enzyme E1 inhibitor TAS4464 in patients with advanced solid tumors.Invest New Drugs. 2021 Aug;39(4):1036-1046. doi: 10.1007/s10637-020-01055-5. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Invest New Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33560503 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
MLN4924, A Neddylation Inhibitor, Improves the Vascular Reactivity but Causes Early Mortality in Polymicrobial Sepsis: Effect on Vascular RhoA/ROCK Signaling.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025 Sep;25(9):1304-1320. doi: 10.1007/s12012-025-10039-x. Epub 2025 Jul 8. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40629201
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
