Eyeglasses based wireless electrolyte and metabolite sensor platform
- PMID: 28470263
- PMCID: PMC5507201
- DOI: 10.1039/c7lc00192d
Eyeglasses based wireless electrolyte and metabolite sensor platform
Abstract
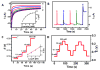
The demand for wearable sensors has grown rapidly in recent years, with increasing attention being given to epidermal chemical sensing. Here, we present the first example of a fully integrated eyeglasses wireless multiplexed chemical sensing platform capable of real-time monitoring of sweat electrolytes and metabolites. The new concept has been realized by integrating an amperometric lactate biosensor and a potentiometric potassium ion-selective electrode into the two nose-bridge pads of the glasses and interfacing them with a wireless electronic backbone placed on the glasses' arms. Simultaneous real-time monitoring of sweat lactate and potassium levels with no apparent cross-talk is demonstrated along with wireless signal transduction. The electrochemical sensors were screen-printed on polyethylene terephthalate (PET) stickers and placed on each side of the glasses' nose pads in order to monitor sweat metabolites and electrolytes. The electronic backbone on the arms of the glasses' frame offers control of the amperometric and potentiometric transducers and enables Bluetooth wireless data transmission to the host device. The new eyeglasses system offers an interchangeable-sensor feature in connection with a variety of different nose-bridge amperometric and potentiometric sensor stickers. For example, the lactate bridge-pad sensor was replaced with a glucose one to offer convenient monitoring of sweat glucose. Such a fully integrated wireless "Lab-on-a-Glass" multiplexed biosensor platform can be readily expanded for the simultaneous monitoring of additional sweat electrolytes and metabolites.
Figures



References
-
- Bandodkar AJ, Wang J. Trends Biotechnol. 2014;32:363–371. - PubMed
-
- Mukhopadhyay SC. IEEE Sens J. 2015;15:1321–1330.
-
- Bandodkar AJ, Jia W, Wang J. Electroanalysis. 2015;27:1–12.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

