Targeting mannose receptor expression on macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques of apolipoprotein E-knockout mice using 111In-tilmanocept
- PMID: 28470406
- PMCID: PMC5415447
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-017-0287-y
Targeting mannose receptor expression on macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques of apolipoprotein E-knockout mice using 111In-tilmanocept
Abstract
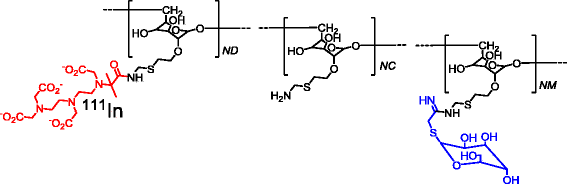
Background: Atherosclerotic plaque phenotypes are classified based on the extent of macrophage infiltration into the lesions, and the presence of certain macrophage subsets might be a sign for plaque vulnerability. The mannose receptor (MR) is over-expressed in activated macrophages. Tilmanocept is a tracer that targets MR and is approved in Europe and the USA for the detection of sentinel lymph nodes. In this study, our aim was to evaluate the potential of 111In-labelled tilmanocept for the detection of MR-positive macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques of apolipoprotein E-knockout (ApoE-KO) mouse model.
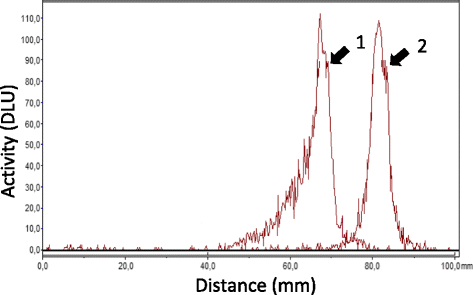
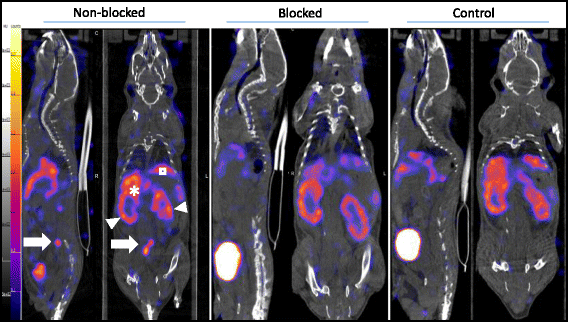
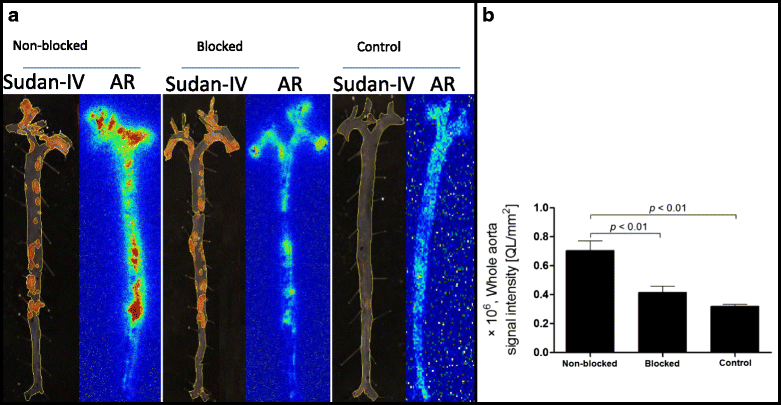
Methods: Tilmanocept was labelled with 111In. The labelling stability and biodistribution of the tracer was first evaluated in control mice (n = 10) 1 h post injection (p.i.). For in vivo imaging studies, 111In-tilmanocept was injected into ApoE-KO (n = 8) and control (n = 8) mice intravenously (i.v.). The mice were scanned 90 min p.i. using a dedicated animal SPECT/CT. For testing the specificity of 111In-tilmanocept uptake in plaques, a group of ApoE-KO mice was co-injected with excess amount of non-labelled tilmanocept. For ex vivo imaging studies, the whole aortas (n = 9 from ApoE-KO and n = 4 from control mice) were harvested free from adventitial tissue for Sudan IV staining and autoradiography. Cryosections were prepared for immunohistochemistry (IHC).
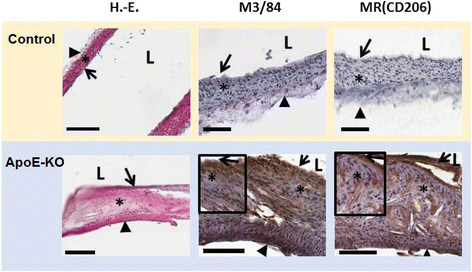
Results: 111In radiolabelling of tilmanocept provided a yield of greater than 99%. After i.v. injection, 111In-tilmanocept accumulated in vivo in MR-expressing organs (i.e. liver and spleen) and showed only low residual blood signal 1 h p.i. MR-binding specificity in receptor-positive organs was demonstrated by a 1.5- to 3-fold reduced uptake of 111In-tilmanocept after co-injection of a blocking dose of non-labelled tilmanocept. Focal signal was detected in atherosclerotic plaques of ApoE-KO mice, whereas no signal was detected in the aortas of control mice. 111In-tilmanocept uptake was detected in atherosclerotic plaques on autoradiography correlating well with Sudan IV-positive areas and associating with subendothelial accumulations of MR-positive macrophages as demonstrated by IHC.
Conclusions: After i.v. injection, 111In-tilmanocept accumulated in MR-expressing organs and was associated with only low residual blood signal. In addition, 111In-tilmanocept uptake was detected in atherosclerotic plaques of mice containing MR-expressing macrophages suggesting that tilmanocept represents a promising tracer for the non-invasive detection of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Inflammation; M2 differentiated macrophages; Non-invasive imaging; SPECT/CT; Tilmanocept.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting mannose receptor expression on macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques of apolipoprotein E-knockout mice using 68Ga-NOTA-anti-MMR nanobody: non-invasive imaging of atherosclerotic plaques.EJNMMI Res. 2019 Jan 21;9(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13550-019-0474-0. EJNMMI Res. 2019. PMID: 30666513 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging atherosclerotic plaques by targeting Galectin-3 and activated macrophages using (89Zr)-DFO- Galectin3-F(ab')2 mAb.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(4):1864-1876. doi: 10.7150/thno.50247. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33408786 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of [99mTc]Radiolabeled Macrophage Mannose Receptor-Specific Nanobodies for Targeting of Atherosclerotic Lesions in Mice.Mol Imaging Biol. 2018 Apr;20(2):260-267. doi: 10.1007/s11307-017-1117-3. Mol Imaging Biol. 2018. PMID: 28875290
-
Development of 111In-labeled liposomes for vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque imaging.J Nucl Med. 2014 Jan;55(1):115-20. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.113.123158. Epub 2013 Dec 12. J Nucl Med. 2014. PMID: 24337605
-
The inextricable axis of targeted diagnostic imaging and therapy: An immunological natural history approach.Nucl Med Biol. 2016 Mar;43(3):215-25. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2015.11.007. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Nucl Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26924502 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The biological applications of near-infrared optical nanomaterials in atherosclerosis.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Aug 12;22(1):478. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02703-1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39135099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Nuclear Medicine Imaging of Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation.J Imaging. 2022 Sep 27;8(10):261. doi: 10.3390/jimaging8100261. J Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36286355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody-Based Tracers for PET/SPECT Imaging of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases.Chembiochem. 2019 Feb 15;20(4):422-436. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201800429. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Chembiochem. 2019. PMID: 30240550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiopharmaceuticals for PET and SPECT Imaging: A Literature Review over the Last Decade.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 30;23(9):5023. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095023. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563414 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives on Small Animal Radionuclide Imaging; Considerations and Advances in Atherosclerosis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2019 Mar 11;6:39. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00039. eCollection 2019. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30915335 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

