Carbohydrate recognition by the rhamnose-binding lectin SUL-I with a novel three-domain structure isolated from the venom of globiferous pedicellariae of the flower sea urchin Toxopneustes pileolus
- PMID: 28470711
- PMCID: PMC5521583
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3185
Carbohydrate recognition by the rhamnose-binding lectin SUL-I with a novel three-domain structure isolated from the venom of globiferous pedicellariae of the flower sea urchin Toxopneustes pileolus
Abstract
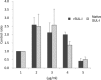
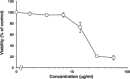
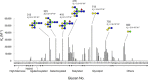
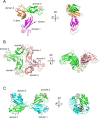
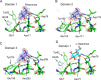
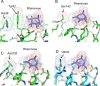
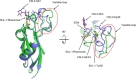
The globiferous pedicellariae of the venomous sea urchin Toxopneustes pileolus contains several biologically active proteins. We have cloned the cDNA of one of the toxin components, SUL-I, which is a rhamnose-binding lectin (RBL) that acts as a mitogen through binding to carbohydrate chains on target cells. Recombinant SUL-I (rSUL-I) was produced in Escherichia coli cells, and its carbohydrate-binding specificity was examined with the glycoconjugate microarray analysis, which suggested that potential target carbohydrate structures are galactose-terminated N-glycans. rSUL-I exhibited mitogenic activity for murine splenocyte cells and toxicity against Vero cells. The three-dimensional structure of the rSUL-I/l-rhamnose complex was determined by X-ray crystallographic analysis at a 1.8 Å resolution. The overall structure of rSUL-I is composed of three distinctive domains with a folding structure similar to those of CSL3, a RBL from chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) eggs. The bound l-rhamnose molecules are mainly recognized by rSUL-I through hydrogen bonds between its 2-, 3-, and 4-hydroxy groups and Asp, Asn, and Glu residues in the binding sites, while Tyr and Ser residues participate in the recognition mechanism. It was also inferred that SUL-I may form a dimer in solution based on the molecular size estimated via dynamic light scattering as well as possible contact regions in its crystal structure.
Keywords: X-ray crystallographic analysis; lectin; rhamnose; sea urchin; toxin.
© 2017 The Protein Society.
Figures



References
-
- Nakagawa H, Tanigawa T, Tomita K, Tomihara Y, Araki Y, Tachikawa E (2003) Recent studies on the phathological effects of purified sea urchin toxins. J Toxicol 22:633–649.
-
- Takei M, Nakagawa H (2006) A sea urchin lectin, SUL‐1, from the toxopneustid sea urchin induces DC maturation from human monocyte and drives Th1 polirization in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 213:27–36. - PubMed
-
- Edo K, Sakai H, Nakagawa H, Hashimoto T, Shinohara M, Ohura K (2012) Immunomodulatory activity of a pedicellarial venom lectin from the toxopneustid sea urchin, Toxopneustes pileolus . Toxin Rev 31:54–60.
-
- Tateno H (2010) SUEL‐related lectins, a lectin family widely distributed throughout organisms. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 74:1141–1144. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

