Comparison of fast acquisition strategies in whole-heart four-dimensional flow cardiac MR: Two-center, 1.5 Tesla, phantom and in vivo validation study
- PMID: 28470915
- PMCID: PMC5801550
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.25746
Comparison of fast acquisition strategies in whole-heart four-dimensional flow cardiac MR: Two-center, 1.5 Tesla, phantom and in vivo validation study
Abstract
Purpose: To validate three widely-used acceleration methods in four-dimensional (4D) flow cardiac MR; segmented 4D-spoiled-gradient-echo (4D-SPGR), 4D-echo-planar-imaging (4D-EPI), and 4D-k-t Broad-use Linear Acquisition Speed-up Technique (4D-k-t BLAST).
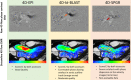
Materials and methods: Acceleration methods were investigated in static/pulsatile phantoms and 25 volunteers on 1.5 Tesla MR systems. In phantoms, flow was quantified by 2D phase-contrast (PC), the three 4D flow methods and the time-beaker flow measurements. The later was used as the reference method. Peak velocity and flow assessment was done by means of all sequences. For peak velocity assessment 2D PC was used as the reference method. For flow assessment, consistency between mitral inflow and aortic outflow was investigated for all pulse-sequences. Visual grading of image quality/artifacts was performed on a four-point-scale (0 = no artifacts; 3 = nonevaluable).
Results: For the pulsatile phantom experiments, the mean error for 2D PC = 1.0 ± 1.1%, 4D-SPGR = 4.9 ± 1.3%, 4D-EPI = 7.6 ± 1.3% and 4D-k-t BLAST = 4.4 ± 1.9%. In vivo, acquisition time was shortest for 4D-EPI (4D-EPI = 8 ± 2 min versus 4D-SPGR = 9 ± 3 min, P < 0.05 and 4D-k-t BLAST = 9 ± 3 min, P = 0.29). 4D-EPI and 4D-k-t BLAST had minimal artifacts, while for 4D-SPGR, 40% of aortic valve/mitral valve (AV/MV) assessments scored 3 (nonevaluable). Peak velocity assessment using 4D-EPI demonstrated best correlation to 2D PC (AV:r = 0.78, P < 0.001; MV:r = 0.71, P < 0.001). Coefficient of variability (CV) for net forward flow (NFF) volume was least for 4D-EPI (7%) (2D PC:11%, 4D-SPGR: 29%, 4D-k-t BLAST: 30%, respectively).
Conclusion: In phantom, all 4D flow techniques demonstrated mean error of less than 8%. 4D-EPI demonstrated the least susceptibility to artifacts, good image quality, modest agreement with the current reference standard for peak intra-cardiac velocities and the highest consistency of intra-cardiac flow quantifications.
Level of evidence: 1 Technical Efficacy: Stage 2 J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018;47:272-281.
Keywords: 4D flow cardiac MR; MR flow imaging; flow quantification; phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging; validation.
© 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures



References
-
- Baltes C, Kozerke S, Hansen MS, Pruessmann KP, Tsao J, Boesiger P. Accelerating cine phase‐contrast flow measurements using k‐t BLAST and k‐t SENSE. Magn Reson Med 2005;54:1430–1438. - PubMed
-
- Stadlbauer A, van der Riet W, Crelier G, Salomonowitz E. Accelerated time‐resolved three‐dimensional MR velocity mapping of blood flow patterns in the aorta using SENSE and k‐t BLAST. Eur J Radiol 2010;75:e15–e21. - PubMed
-
- Lustig M, Donoho D, Pauly JM. Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn Reson Med 2007;58:1182–1195. - PubMed
-
- Davis CP, McKinnon GC, Debatin JF, et al. Normal heart: evaluation with echo‐planar MR imaging. Radiology 1994;191:691–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

