Salivary leptin levels in normal weight and overweight individuals and their correlation with orthodontic tooth movement
- PMID: 28471265
- PMCID: PMC8357200
- DOI: 10.2319/120216-869.1
Salivary leptin levels in normal weight and overweight individuals and their correlation with orthodontic tooth movement
Abstract
Objectives: To assess and compare the concentration of leptin in saliva between normal weight and overweight individuals and to evaluate the rate of orthodontic tooth movement.
Materials and methods: Thirty female subjects were divided into two groups: I (normal weight) and II (overweight group) based on their body mass index. All subjects underwent fixed appliance therapy requiring upper first premolar extraction and distal movement of the canine. Distal force was applied to the maxillary right canine using active lacebacks. Salivary samples were collected just before force application (T0), 1 hour (T1), and 1 month (T2) after force application. The rate of tooth movement was evaluated over 3 months and was measured on study models.
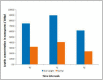
Results: At all three time intervals, mean leptin concentration was greater in overweight individuals than normal weight individuals. In both groups at T1, the mean leptin concentration was found to increase significantly compared with the baseline value (T0), but at T2, the leptin concentration declined to values lesser than the baseline values (T0).
Conclusions: Overweight individuals had greater salivary leptin concentration. There was a positive correlation between salivary leptin concentration and rate of tooth movement in both normal and overweight individuals. The rate of tooth movement is decreased in overweight individuals as compared with normal weight individuals.
Keywords: Orthodontic tooth movement; Salivary leptin levels.
Figures
Comment in
-
Letters From Our ReadersTo: Editor, The Angle Orthodontist Re: Salivary leptin levels in normal weight and overweight individuals and their correlation with orthodontic tooth movement. By Tamizhmani Jayachandran, Bhadrinath Srinivasan, Sridevi Padmanabhan. Angle Orthod. 2017;87:739-744.Angle Orthod. 2018 Mar;88(2):248. doi: 10.2319/0003-3219-88.2.248. Angle Orthod. 2018. PMID: 29470131 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Letters From Our ReadersTo: Editor, The Angle Orthodontist. Re: Salivary leptin levels in normal weight and overweight individuals and their correlation with orthodontic tooth movement. Tamizhmani Jayachandran, Bhadrinath Srinivasan, Sridevi Padmanabhan. The Angle Orthodontist. 2017; 87: 739-744.Angle Orthod. 2018 Mar;88(2):247. doi: 10.2319/0003-3219-88.2.247. Angle Orthod. 2018. PMID: 29470132 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Krishnan V, Davidovitch Z. Cellular, molecular, and tissue-level reactions to orthodontic force. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006;129:469e.1–32. - PubMed
-
- Alhashimi N, Frithiof L, Brudvik P, Bakhiet M. Orthodontic tooth movement and de novo synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2001;119:307–312. - PubMed
-
- Lee KJ, Park YC, Yu HS, Choi SH, Yoo YJ. Effects of continuous and interrupted orthodontic force on interleukin-1β and prostaglandin E2 production in gingival crevicular fluid. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004;125:168–167. - PubMed
-
- Grieve WG, Johnson GK, Moore RN, Reinhardt RA, DuBois LM. Prostaglandin E (PGE) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) levels in gingival crevicular fluid during human orthodontic tooth movement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1994;105:369–374. - PubMed
-
- Tuncer BB, Ozmeriç N, Tuncer C, et al. Levels of interleukin-8 during tooth movement. Angle Orthod. 2005;75:631–636. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical