The clinical significance of sCD14-ST for blood biomarker in neonatal hematosepsis: A diagnostic accuracy study
- PMID: 28471985
- PMCID: PMC5419931
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006823
The clinical significance of sCD14-ST for blood biomarker in neonatal hematosepsis: A diagnostic accuracy study
Abstract
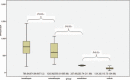
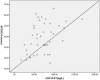
Hematosepsis is a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) with suspected or confirmed infection, which is the most common infectious disease in clinical neonatal intensive care unit. As the rapid development of neonatal hematosepsis caused by various basic diseases, the mortality rate is high, and there are some sequelae.We report the lasted study to date with 96 cases from Fujian Longyan First Hospital between 2013 and 2015. The aim of our study is to explore the value of soluble cluster of differentiation 14 subtype (sCD14-ST) in whole blood for differential diagnosis of neonatal hematosepsis at an early stage, and used in evaluation of the severity about sepsis combined with acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II (APACHE-II) score, procalcitonin (PCT), C reactive protein (CRP), and leukocyte (WBC).In our cohort, all cases met the diagnostic criteria for hematosepsis specific for newborns. We selected 42 neonates with hematosepsis, 54 neonates with nonhematosepsis, 44 noninfectious SIRS neonates, and 53 healthy neonatal controls. Which were determined the sCD14-ST, PCT, CRP, and WBC of all samples before treatment. Then assign the APACHE-II score for the all samples before and after treatment.The study shows, sCD14-ST levels were significantly higher in hematosepsis than nonhematosepsis group (t = -2.112, P = .041). Meanwhile, sCD14-ST levels were significantly higher in neonatal hematosepsis than in noninfectious SIRS group and controls (χ = 57.812, 68.944, P < .01). However, sCD14-ST in hematosepsis group was positively correlated with APACHE-II score (R-value = 0.415, P < .01). During treatment, the sCD14-ST level was decreased obviously along with APACHE-II score, PCT, CRP, and WBC (χ = 35.019, 78.399, 52.363, 25.912, 7.252, all P values <.01). The area under the curve (AUC) of sCD14-ST was 0.942. The differences in ROC of sCD14-ST compared with PCT, CRP, and WBC were statistically significant (Z = -6.034, -4.474, -5.722, all P values <.01). The sensitivity and specificity of sCD14-ST were 95.2% and 84.9%, respectively.sCD14-ST could be a blood biomarker for early identification and disease valuation in newborns hematosepsis infection; and its diagnostic value is superior to other laboratory indexes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Aly H, Herson V, Duncan A, et al. Is bloodstream infection preventable among premature infants. A tale of two cities. Pediatrics 2005;115:1513–8. - PubMed
-
- Liu T, Chen HW, Liang DY, et al. Progress of prognostic markers in sepsis. Int J Lab Med 2014;35:2794–6.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

