Persistent low serum zinc is associated with recurrent sepsis in critically ill patients - A pilot study
- PMID: 28472045
- PMCID: PMC5417428
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176069
Persistent low serum zinc is associated with recurrent sepsis in critically ill patients - A pilot study
Abstract
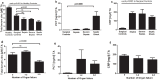
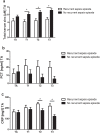
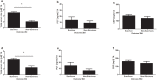
Zinc is an essential trace element for both pathogens and hosts. Hypozincemia is a well known phenomenon in sepsis patients and represents the innate immune systems attempt to deprive pathogens of zinc. However little is known about course, restitution and prognostic value of serum zinc levels in sepsis patients. We performed a prospective observational single-center study set in a tertiary care university hospital intensive care unit. Serum zinc levels were singularly measured of healthy controls and sequentially of surgical sepsis patients and surgical patients over a 8-day period. Throughout the study period, we report significantly decreased serum zinc levels in surgical and surgical sepsis patients compared to healthy controls. Lower serum zinc levels in surgical sepsis patients were associated with a higher susceptibility to a recurrent sepsis episode. Furthermore, surgical sepsis patients with a higher number of organ dysfunctions and increased in-hospital mortality at day 28 and 90 showed lower serum zinc levels at admission. We report serum zinc levels as a promising biomarker in the diagnosis and evaluation of sepsis patients. However, it is still unclear whether these findings are caused by an over-amplified redistribution of zinc during acute-phase response, or whether the critically ill patients were zinc deficient before sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29(7):1303–10. - PubMed
-
- Garnacho-Montero J, Garcia-Garmendia JL, Barrero-Almodovar A, Jimenez-Jimenez FJ, Perez-Paredes C, Ortiz-Leyba C. Impact of adequate empirical antibiotic therapy on the outcome of patients admitted to the intensive care unit with sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2003;31(12):2742–51. Epub 2003/12/12. 10.1097/01.CCM.0000098031.24329.10 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shanbhogue LKR, Paterson N. Effect of Sepsis and Surgery on Trace Minerals. Jpen-Parenter Enter. 1990;14(3):287–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

