Plasminogen activator activity in tears of pregnant women
- PMID: 28472076
- PMCID: PMC5417609
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177003
Plasminogen activator activity in tears of pregnant women
Abstract
Purpose: Plasminogen activator activity (PAA) in tears of pregnant women was investigated at various gestation times to assess the availability of plasminogen activator for aiding potential corneal wound healing processes during pregnancy.
Methods: PAA was measured by a spectrophotometric method. The analysis used 91 tear samples from pregnant and non-pregnant women, supplemented with 10 additional tear PAA measurements from non-pregnant women obtained in a previous study.
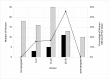
Results: Tear levels of PAA in pregnant women formed a bimodal distribution. Either the tear PAA level was zero or non-zero during pregnancy. When non-zero, the tear PAA level was dissociated from gestation time and not different than non-pregnant and post-pregnant levels. The frequency of occurrence of zero level tear PAA increased with gestation: 16%, 17% and 46% had zero tear PAA in samples taken from women in the first, second and third trimester, respectively.
Conclusions: Overall, of the tear samples taken from women during pregnancy, a total of 26% were at zero tear PAA. The remaining tear samples had non-zero tear PAA values throughout gestation equivalent to non-pregnant tear PAA values, suggesting local control of the source of PAA in tears. Given the importance of the plasminogen activator system in tears to wound healing in the cornea, and the high occurrence of zero tear PAA in our sample of pregnant women, elective corneal surgery would be contraindicated. If corneal surgery is nevertheless necessary, the tear PAA level would be worth checking and patients with low level should be closely observed during the postoperative period.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasminogen activator activity and inhibition in rabbit tears after photorefractive keratectomy.Exp Eye Res. 2003 Dec;77(6):675-80. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2003.08.012. Exp Eye Res. 2003. PMID: 14609555
-
Plasminogen activator activity in tears after excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000 Nov;41(12):3743-7. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000. PMID: 11053271
-
Determination of plasminogen activator activities in normal and pathological human tears. The significance of tear plasminogen activators in the inflammatory and traumatic lesions of the cornea and the conjunctiva.Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1990 Oct;68(5):508-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1990.tb04778.x. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1990. PMID: 2275342
-
Plasmin and plasminogen activator activities in tear fluid during corneal wound healing after anterior keratectomy.Curr Eye Res. 1989 Dec;8(12):1293-8. doi: 10.3109/02713688909013909. Curr Eye Res. 1989. PMID: 2534068
-
Proteinases of the cornea and preocular tear film.Vet Ophthalmol. 2007 Jul-Aug;10(4):199-206. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-5224.2007.00546.x. Vet Ophthalmol. 2007. PMID: 17565550 Review.
Cited by
-
Laboratory Testing of Hemostasis in Pregnancy: A Brief Overview.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2663:111-125. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3175-1_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37204707 Review.
-
A Retrospective Assessment of Thrombophilia in Pregnant Women with First and Second Trimester Pregnancy Loss.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 8;19(24):16500. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416500. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36554381 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of chitosan-g-PEG grafted nanoparticles as a half-life enhancer carrier for tissue plasminogen activator delivery.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020 Dec;14(9):899-907. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2019.0304. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33399124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hellgren M. Hemostasis during normal pregnancy and puerperium. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2003;29(2):125–30. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-38897 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brenner B. Haemostatic changes in pregnancy. Thromb Res. 2004;114:409–414. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2004.08.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sulniute R, Shen Y, Guo YZ, Fallah M, Ahlskog N, Ny L, et al. Plasminogen is a critical regulator of cutaneous wound healing. Thromb Haemost. 2016;115(5):1001–1009. doi: 10.1160/TH15-08-0653 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kruithof EK, Tran-Thang C, Gudinchet A, Hauert J, Nicoloso G, Genton C, et al. Fibrinolysis in pregnancy: a study of plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood. 1987;69(2):460–466. - PubMed
-
- van Wersch JW, Ubachs JM. Blood coagulation and fibrinolysis during normal pregnancy. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1991;29(1):45–50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

