Identifying novel fruit-related genes in Arabidopsis thaliana based on the random walk with restart algorithm
- PMID: 28472169
- PMCID: PMC5417634
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177017
Identifying novel fruit-related genes in Arabidopsis thaliana based on the random walk with restart algorithm
Abstract
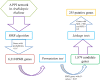
Fruit is essential for plant reproduction and is responsible for protection and dispersal of seeds. The development and maturation of fruit is tightly regulated by numerous genetic factors that respond to environmental and internal stimulation. In this study, we attempted to identify novel fruit-related genes in a model organism, Arabidopsis thaliana, using a computational method. Based on validated fruit-related genes, the random walk with restart (RWR) algorithm was applied on a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network using these genes as seeds. The identified genes with high probabilities were filtered by the permutation test and linkage tests. In the permutation test, the genes that were selected due to the structure of the PPI network were discarded. In the linkage tests, the importance of each candidate gene was measured from two aspects: (1) its functional associations with validated genes and (2) its similarity with validated genes on gene ontology (GO) terms and KEGG pathways. Finally, 255 inferred genes were obtained, subsequent extensive analysis of important genes revealed that they mainly contribute to ubiquitination (UBQ9, UBQ8, UBQ11, UBQ10), serine hydroxymethyl transfer (SHM7, SHM5, SHM6) or glycol-metabolism (HXKL2_ARATH, CSY5, GAPCP1), suggesting essential roles during the development and maturation of fruit in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Network-based method for mining novel HPV infection related genes using random walk with restart algorithm.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Jun;1864(6 Pt B):2376-2383. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.11.021. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 29197659
-
A Shortest-Path-Based Method for the Analysis and Prediction of Fruit-Related Genes in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 19;11(7):e0159519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159519. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27434024 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of genes related to proliferative diabetic retinopathy through RWR algorithm based on protein-protein interaction network.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Jun;1864(6 Pt B):2369-2375. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.11.017. Epub 2017 Dec 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 29237571
-
Drawing lines and borders: how the dehiscent fruit of Arabidopsis is patterned.Bioessays. 2005 Jan;27(1):42-9. doi: 10.1002/bies.20165. Bioessays. 2005. PMID: 15612035 Review.
-
Flower and fruit development in Arabidopsis thaliana.Int J Dev Biol. 2005;49(5-6):633-43. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.052020pr. Int J Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 16096970 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of COVID-19 Infection-Related Human Genes Based on a Random Walk Model in a Virus-Human Protein Interaction Network.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jul 8;2020:4256301. doi: 10.1155/2020/4256301. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32685484 Free PMC article.
-
Large Scale Proteomic Data and Network-Based Systems Biology Approaches to Explore the Plant World.Proteomes. 2018 Jun 3;6(2):27. doi: 10.3390/proteomes6020027. Proteomes. 2018. PMID: 29865292 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring novel genes related to colorectal cancer via random walk with restart algorithm.Gene Ther. 2019 Sep;26(9):373-385. doi: 10.1038/s41434-019-0090-7. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Gene Ther. 2019. PMID: 31308477
-
Genome-Wide Characterization and Gene Expression Analyses of Malate Dehydrogenase (MDH) Genes in Low-Phosphorus Stress Tolerance of Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 23;24(5):4414. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054414. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901845 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic control of the operculum and capsule morphology of Eucalyptus globulus.Ann Bot. 2022 Jul 19;130(1):97-108. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcac072. Ann Bot. 2022. PMID: 35652517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang GZ, Jin SH, Jiang XY, Dong RR, Li P, Li YJ, et al. Ectopic expression of UGT75D1, a glycosyltransferase preferring indole-3-butyric acid, modulates cotyledon development and stress tolerance in seed germination of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol. 2016;90(1–2):77–93. 10.1007/s11103-015-0395-x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang WQ, Song BY, Deng ZJ, Wang Y, Liu SJ, Moller IM, et al. Proteomic Analysis of Lettuce Seed Germination and Thermoinhibition by Sampling of Individual Seeds at Germination and Removal of Storage Proteins by Polyethylene Glycol Fractionation. Plant Physiol. 2015;167(4):1332–U380. 10.1104/pp.15.00045 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leeggangers HACF, Folta A, Muras A, Nap JP, Mlynarova L. Reduced seed germination in Arabidopsis over-expressing SWI/SNF2 ATPase genes. Physiol Plantarum. 2015;153(2):318–26. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases