Anatomy and Surgical Approaches to the Rabbit Nasal Septum
- PMID: 28472203
- PMCID: PMC5710630
- DOI: 10.1001/jamafacial.2017.0116
Anatomy and Surgical Approaches to the Rabbit Nasal Septum
Abstract
Importance: The rabbit is the primary animal model used to investigate aspects of nasal surgery. Although several studies have used this model, none has provided a comprehensive analysis of the surgical anatomy and techniques used to gain access to the rabbit nasal fossae and septum.
Objective: To describe and optimize the surgical anatomy and approach to the rabbit nasal vault and septal cartilage.
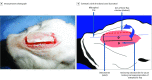
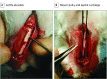
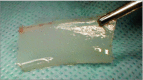
Design, setting, and participants: In an ex vivo animal study conducted at an academic medical center, preliminary cadaveric dissections were performed on rabbit head specimens to establish familiarity with relevant anatomy and rehearse various approaches. Live Pasteurella-free New Zealand white rabbits (3.5-4.0 kg) were used to further develop this surgical technique developed here. Access of the nasal vault was gained through a midline nasal dorsum incision and creation of an osteoplastic flap with a drill. Submucosal resection was performed with preservation of the mucoperichondrium. All rabbits were monitored daily for 4 weeks in the postoperative period for signs of infection, pain, and complications. The study was conducted from June 1, 2014, to December 1, 2014.
Main outcomes and measures: Surgical anatomy and techniques used to gain access to the rabbit nasal vault and harvest septal cartilage.
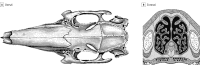
Results: Four Pasteurella-free New Zealand white rabbits (Western Organ Rabbit Co), ranging in age from 9 to 12 months and weighing between 3.5 and 4.0 kg, were used in this study. Initial dissections demonstrated the feasibility of harvesting septal cartilage while preserving the mucoperichondrial envelope. Access to the nasal vault through this 3-osteotomy approach allowed for maximal exposure to the nasal cavity bilaterally while maintaining the integrity of the mucoperichondrium following septal cartilage harvest. The maximum amount of bulk, en bloc, cartilage harvested was 1.0 × 2.5 cm. Following surgical dissection, all animals maintained adequate airway patency and support to midface structures. Furthermore, all specimens preserved the integrity of the mucoperichondrium, septum, vascular anatomy, and airway dynamics. No operative complications, postoperative airway compromise, or infections were observed.
Conclusions and relevance: Access to the rabbit nasal vault and septal cartilage is feasible through a variety of surgical approaches and techniques. To date, this is the first study to meticulously document and review the surgical approaches to the rabbit nasal cavity. This approach describes a novel, 3-osteotomy method of accessing the nasal cavity bilaterally and successfully harvesting rabbit septal cartilage in a submucoperichondrial plane. The ability to preserve native anatomy and function allows for improved outcomes in translational and animal guided clinical research.
Level of evidence: NA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Nolst Trenité GJ, Verwoerd CDA, Verwoerd-Verhoef HL. Reimplantation of autologous septal cartilage in the growing nasal septum: II—the influence of reimplantation of rotated or crushed autologous septal cartilage on nasal growth: an experimental study in growing rabbits. Rhinology. 1988;26(1):25-32. - PubMed
-
- Nolst Trenité GJ, Verwoerd CD, Verwoerd-Verhoef HL. Reimplantation of autologous septal cartilage in the growing nasal septum: I—the influence of resection and reimplantation of septal cartilage upon nasal growth: an experimental study in rabbits. Rhinology. 1987;25(4):225-236. - PubMed
-
- Verwoerd CDA, Urbanus NAM, Nijdam DC. The effects of septal surgery on the growth of nose and maxilla. Rhinology. 1979;17(2):53-63. - PubMed
-
- Verwoerd CD, Verwoerd-Verhoef HL. Developmental aspects of the deviated nose. Facial Plast Surg. 1989;6(2):95-100. - PubMed
-
- Verwoerd CD, Urbanus NA, Mastenbroek GJ. The influence of partial resections of the nasal septal cartilage on the growth of the upper jaw and the nose: an experimental study in rabbits. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1980;5(5):291-302. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
