Are Lowered Socioeconomic Circumstances Causally Related to Tooth Loss? A Natural Experiment Involving the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake
- PMID: 28472254
- PMCID: PMC5859979
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwx059
Are Lowered Socioeconomic Circumstances Causally Related to Tooth Loss? A Natural Experiment Involving the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake
Abstract
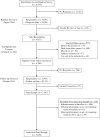
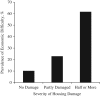
Oral health status is correlated with socioeconomic status. However, the causal nature of the relationship is not established. Here we describe a natural experiment involving deteriorating socioeconomic circumstances following exposure to the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami. We investigated the relationship between subjective economic deterioration and housing damage due to the disaster and tooth loss in a cohort of community-dwelling residents (n = 3,039), from whom we obtained information about socioeconomic status and health status in 2010 (i.e., predating the disaster). A follow-up survey was performed in 2013 (postdisaster), and 82.1% of the 4,380 eligible survivors responded. We estimated the impact of subjective economic deterioration and housing damage due to the disaster on tooth loss by fitting an instrumental variable probit model. Subjective economic deterioration and housing damage due to the disaster were significantly associated with 8.1% and 1.7% increases in the probability of tooth loss (probit coefficients were 0.469 (95% confidence interval: 0.065, 0.872) and 0.103 (95% confidence interval: 0.011, 0.196), respectively). In this natural experiment, we confirmed the causal relationship between deteriorating socioeconomic circumstances and tooth loss.
Keywords: change in economic status; instrumental variable analyses; natural disaster; natural experiment; oral health; tooth loss.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Listl S, Galloway J, Mossey PA, et al. Global economic impact of dental diseases. J Dent Res. 2015;94(10):1355–1361. - PubMed
-
- Marshman Z, Robinson PG. Dental public health In: Detels R, Beaglehole R, Lansang MA, et al., eds. Oxford Textbook of Public Health. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford Medical Publications; 2011:1101–1116.
-
- Daly B, Batchelor P, Treasure E, et al. Essential Dental Public Health. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press; 2013.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

