Human Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody Inhibition of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication in the Common Marmoset
- PMID: 28472421
- PMCID: PMC7107363
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jix209
Human Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody Inhibition of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication in the Common Marmoset
Abstract
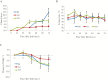
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection in humans is highly lethal, with a fatality rate of 35%. New prophylactic and therapeutic strategies to combat human infections are urgently needed. We isolated a fully human neutralizing antibody, MCA1, from a human survivor. The antibody recognizes the receptor-binding domain of MERS-CoV S glycoprotein and interferes with the interaction between viral S and the human cellular receptor human dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4). To our knowledge, this study is the first to report a human neutralizing monoclonal antibody that completely inhibits MERS-CoV replication in common marmosets. Monotherapy with MCA1 represents a potential alternative treatment for human infections with MERS-CoV worthy of evaluation in clinical settings.
Keywords: MERS-CoV; common marmoset; human monoclonal antibody.
© Crown copyright 2017.
Figures



References
-
- Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med 2012; 367:1814–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

