Using a Medical Intranet of Things System to Prevent Bed Falls in an Acute Care Hospital: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 28473306
- PMCID: PMC5438463
- DOI: 10.2196/jmir.7131
Using a Medical Intranet of Things System to Prevent Bed Falls in an Acute Care Hospital: A Pilot Study
Abstract
Background: Hospitalized patients in the United States experience falls at a rate of 2.6 to 17.1 per 1000 patient-days, with the majority occurring when a patient is moving to, from, and around the bed. Each fall with injury costs an average of US $14,000.
Objective: The aim was to conduct a technology evaluation, including feasibility, usability, and user experience, of a medical sensor-based Intranet of things (IoT) system in facilitating nursing response to bed exits in an acute care hospital.
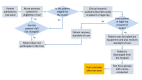
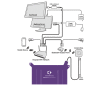
Methods: Patients 18 years and older with a Morse fall score of 45 or greater were recruited from a 35-bed medical-surgical ward in a 317-bed Massachusetts teaching hospital. Eligible patients were recruited between August 4, 2015 and July 31, 2016. Participants received a sensor pad placed between the top of their mattress and bed sheet. The sensor pad was positioned to monitor movement from patients' shoulders to their thighs. The SensableCare System was evaluated for monitoring patient movement and delivering timely alerts to nursing staff via mobile devices when there appeared to be a bed-exit attempt. Sensor pad data were collected automatically from the system. The primary outcomes included number of falls, time to turn off bed-exit alerts, and the number of attempted bed-exit events. Data on patient falls were collected by clinical research assistants and confirmed with the unit nurse manager. Explanatory variables included room locations (zones 1-3), day of the week, nursing shift, and Morse Fall Scale (ie, positive fall history, positive secondary diagnosis, positive ambulatory aid, weak impaired gait/transfer, positive IV/saline lock, mentally forgets limitations). We also assessed user experience via nurse focus groups. Qualitative data regarding staff interactions with the system were collected during two focus groups with 25 total nurses, each lasting approximately 1.5 hours.
Results: A total of 91 patients used the system for 234.0 patient-days and experienced no bed falls during the study period. On average, patients were assisted/returned to bed 46 seconds after the alert system was triggered. Response times were longer during the overnight nursing shift versus day shift (P=.005), but were independent of the patient's location on the unit. Focus groups revealed that nurses found the system integrated well into the clinical nursing workflow and the alerts were helpful in patient monitoring.
Conclusions: A medical IoT system can be integrated into the existing nursing workflow and may reduce patient bed fall risk in acute care hospitals, a high priority but an elusive patient safety challenge. By using an alerting system that sends notifications directly to nurses' mobile devices, nurses can equally respond to unassisted bed-exit attempts wherever patients are located on the ward. Further study, including a fully powered randomized controlled trial, is needed to assess effectiveness across hospital settings.
Keywords: accidental falls; acute care; health care technology; health technology assessment; mobile apps; nursing; patient monitoring; patient safety; patient-centered care; sensor devices and platforms.
©Henri U Balaguera, Diana Wise, Chun Yin Ng, Han-Wen Tso, Wan-Lin Chiang, Aimee M Hutchinson, Tracy Galvin, Lee Hilborne, Cathy Hoffman, Chi-Cheng Huang, C Jason Wang. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (http://www.jmir.org), 04.05.2017.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: MedicusTek, the maker of the medical sensor-based Intranet of things, was the sponsor for this study at Lahey Hospital and Medical Center. Several of the authors are affiliated with MedicusTek: Diana Wise, Chun Yin Ng, Han-Wen Tso, and Wan-Lin Chiang are employed by MedicusTek. Drs C Jason Wang, Lee Hilborne, and Chi-Cheng Huang are scientific advisors at MedicusTek.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Technology Assessment: Early Sense for Monitoring Vital Signs in Hospitalized Patients [Internet].Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2016 May. Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2016 May. PMID: 27606394 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Enhancing Patient Safety Through an Integrated Internet of Things Patient Care System: Large Quasi-Experimental Study on Fall Prevention.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Oct 3;26:e58380. doi: 10.2196/58380. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39361417 Free PMC article.
-
US and Dutch nurse experiences with fall prevention technology within nursing home environment and workflow: A qualitative study.Geriatr Nurs. 2017 Jul-Aug;38(4):276-282. doi: 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Dec 10. Geriatr Nurs. 2017. PMID: 27956058 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Sensor Technology to Detect Fall Risk and Prevent Falls in Acute Care.Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2017 Aug;43(8):414-421. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjq.2017.05.003. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2017. PMID: 28738987
-
Technology to promote safe mobility in the elderly.Nurs Clin North Am. 2004 Sep;39(3):649-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cnur.2004.05.001. Nurs Clin North Am. 2004. PMID: 15331307 Review.
Cited by
-
Preventing Falls in Hospitalized Patients: State of the Science.Clin Geriatr Med. 2019 May;35(2):273-283. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2019.01.007. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Clin Geriatr Med. 2019. PMID: 30929888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Internet of things in healthcare for patient safety: an empirical study.BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 Mar 1;22(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-07620-3. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022. PMID: 35232433 Free PMC article.
-
Falls in a single brain rehabilitation center: a 3-year retrospective chart review.Front Neurol. 2025 Feb 24;16:1519555. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1519555. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40066305 Free PMC article.
-
Nurses' Perspectives and Experiences of Using a Bed-Exit Information System in an Acute Hospital Setting: Mixed Methods Study.JMIR Form Res. 2025 Feb 5;9:e64444. doi: 10.2196/64444. JMIR Form Res. 2025. PMID: 39908092 Free PMC article.
-
ROMI: A Real-Time Optical Digit Recognition Embedded System for Monitoring Patients in Intensive Care Units.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 5;23(2):638. doi: 10.3390/s23020638. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Butcher L. The no-fall zone. Hosp Health Netw. 2013 Jun;87(6):26–30. - PubMed
-
- Bouldin EL, Andresen EM, Dunton NE, Simon M, Waters TM, Liu M, Daniels MJ, Mion LC, Shorr RI. Falls among adult patients hospitalized in the United States: prevalence and trends. J Patient Saf. 2013 Mar;9(1):13–17. doi: 10.1097/PTS.0b013e3182699b64. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/23143749 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shorr RI, Mion LC, Chandler AM, Rosenblatt LC, Lynch D, Kessler LA. Improving the capture of fall events in hospitals: combining a service for evaluating inpatient falls with an incident report system. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008 Apr;56(4):701–704. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01605.x. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/18205761 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Joint Commission Preventing falls and fall-related injuries in health care facilities. Sentinel Event Alert. 2015 Sep 28;(55):1–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

