Antineoplastic effects of CPPTL via the ROS/JNK pathway in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 28473664
- PMCID: PMC5503589
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17166
Antineoplastic effects of CPPTL via the ROS/JNK pathway in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
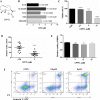
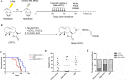
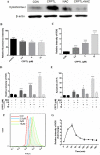
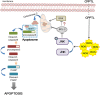
Drug resistance and human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching limit conventional treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Although several small molecule drugs are clinically used, single drug administration is not sufficient to cure AML, which has a high molecular diversity. Metabolic homeostasis plays a key role in determining cellular fate. Appropriate levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) maintain the redox system balance, and excessive amounts of ROS cause oxidative damage, thus providing a strategy to eliminate cancer cells. CPPTL is a novel analogue of parthenolide that exhibited significant cytotoxicity to AML cells in vitro and induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. Additionally, CPPTL's prodrug DMA-CPPTL decreased the burden of AML engraftment and prolonged survival in a mouse model administered human primary AML cells in vivo. CPPTL induced apoptosis of AML cells by stimulating ROS production, and accumulation of ROS then activated the JNK pathway, thereby promoting mitochondrial damage. These results demonstrated that CPPTL effectively eradicated AML cells in vitro and in vivo and suggested that CPPTL may be a novel candidate for auxiliary AML therapy.
Keywords: CPPTL; JNK pathway; ROS; acute myeloid leukemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ethyl acetate extract of Caesalpinia sappan L. inhibited acute myeloid leukemia via ROS-mediated apoptosis and differentiation.Phytomedicine. 2020 Mar;68:153142. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153142. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32045840
-
Therapeutic Effect of V8 Affecting Mitophagy and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Mediated by ROS and CHOP Signaling.FASEB J. 2025 May 15;39(9):e70622. doi: 10.1096/fj.202500599R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40347076
-
Reactive oxygen species activate differentiation gene transcription of acute myeloid leukemia cells via the JNK/c-JUN signaling pathway.Leuk Res. 2018 May;68:112-119. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2018.03.012. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Leuk Res. 2018. PMID: 29609096
-
Analysis of the Mechanisms of Action of Naphthoquinone-Based Anti-Acute Myeloid Leukemia Chemotherapeutics.Molecules. 2019 Aug 28;24(17):3121. doi: 10.3390/molecules24173121. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31466259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and ROS-Mediated Signaling in Leukemia: Novel Promising Perspectives to Eradicate Chemoresistant Cells in Myeloid Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 28;22(5):2470. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052470. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33671113 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting signaling and apoptotic pathways involved in chemotherapeutic drug-resistance of hematopoietic cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 24;8(44):76525-76557. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20408. eCollection 2017 Sep 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29100331 Free PMC article.
-
Parthenolide and Its Soluble Analogues: Multitasking Compounds with Antitumor Properties.Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 21;10(2):514. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020514. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory Signaling Pathways in Preleukemic and Leukemic Stem Cells.Front Oncol. 2017 Nov 13;7:265. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00265. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29181334 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Löwenberg B, Pabst T, Vellenga E, van Putten W, Schouten HC, Graux C, Ferrant A, Sonneveld P, Biemond BJ, Gratwohl A, de Greef GE, Verdonck LF, Schaafsma MR, et al. Cytarabine dose for acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1027–1036. - PubMed
-
- Middeke JM, Fang M, Cornelissen JJ, Mohr B, Appelbaum FR, Stadler M, Sanz J, Baurmann H, Bug G, Schafer-Eckart K, Hegenbart U, Bochtler T, Rollig C, et al. Outcome of patients with abnl(17p) acute myeloid leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2014;123:2960–2967. - PubMed
-
- Yang DH, Lee JJ, Mun YC, Shin HJ, Kim YK, Cho SH, Chung IJ, Seong C, Kim HJ. Predictable prognostic factor of CD56 expression in patients with acute myeloid leukemia with t(8: 21) after high dose cytarabine or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Am J Hematol. 2007;82:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Khwaja A, Bjorkholm M, Gale RE, Levine RL, Jordan CT, Ehninger G, Bloomfield CD, Estey E, Burnett A, Cornelissen JJ, Scheinberg DA, Bouscary D, Linch DC. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16010. - PubMed
-
- Krug U, Röllig C, Koschmieder A, Heinecke A, Sauerland MC, Schaich M, Thiede C, Kramer M, Braess J, Spiekermann K, Haferlach T, Haferlach C, Koschmieder S, et al. Complete remission and early death after intensive chemotherapy in patients aged 60 years or older with acute myeloid leukaemia: a web-based application for prediction of outcomes. The Lancet. 2010;376:2000–2008. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

