Structure aided design of a Neu5Gc specific lectin
- PMID: 28473713
- PMCID: PMC5431456
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-01522-9
Structure aided design of a Neu5Gc specific lectin
Abstract
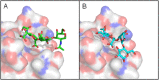
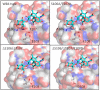
Subtilase cytotoxin (SubAB) of Escherichia coli is an AB5 class bacterial toxin. The pentameric B subunit (SubB) binds the cellular carbohydrate receptor, α2-3-linked N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc). Neu5Gc is not expressed on normal human cells, but is expressed by cancer cells. Elevated Neu5Gc has been observed in breast, ovarian, prostate, colon and lung cancer. The presence of Neu5Gc is prognostically important, and correlates with invasiveness, metastasis and tumour grade. Neu5Gc binding by SubB suggests that it may have utility as a diagnostic tool for the detection Neu5Gc tumor antigens. Native SubB has 20-fold less binding to N-acetlylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac); over 30-fold less if the Neu5Gc linkage was changed from α2-3 to α2-6. Using molecular modeling approaches, site directed mutations were made to reduce the α2-3 [Formula: see text] α2-6-linkage preference, while maintaining or enhancing the selectivity of SubB for Neu5Gc over Neu5Ac. Surface plasmon resonance and glycan array analysis showed that the SubBΔS106/ΔT107 mutant displayed improved specificity towards Neu5Gc and bound to α2-6-linked Neu5Gc. SubBΔS106/ΔT107 could discriminate NeuGc- over Neu5Ac-glycoconjugates in ELISA. These data suggest that improved SubB mutants offer a new tool for the testing of biological samples, particularly serum and other fluids from individuals with cancer or suspected of having cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The following authors (A.W.P., J.C.P., C.J.D. and M.P.J.) declare that they inventors on a provisional patent application on matter contained in this manuscript that will be filed soon.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Specificity and utility of SubB2M, a new N-glycolylneuraminic acid lectin.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jun 7;500(3):765-771. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.151. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29684349
-
Incorporation of a non-human glycan mediates human susceptibility to a bacterial toxin.Nature. 2008 Dec 4;456(7222):648-52. doi: 10.1038/nature07428. Epub 2008 Oct 29. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18971931 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of N-glycolylneuraminic acid biomarkers in sera from patients with ovarian cancer using an engineered N-glycolylneuraminic acid-specific lectin SubB2M.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Dec 9;507(1-4):173-177. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Nov 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30415777
-
N-Glycolylneuraminic acid in human tumours.Biochimie. 2001 Jul;83(7):623-34. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(01)01303-7. Biochimie. 2001. PMID: 11522391 Review.
-
[Functional analysis of glyco-molecules that bind with influenza virus].Uirusu. 2016;66(1):101-116. doi: 10.2222/jsv.66.101. Uirusu. 2016. PMID: 28484173 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Natural and Synthetic Sialylated Glycan Microarrays and Their Applications.Front Mol Biosci. 2019 Sep 13;6:88. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00088. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31572731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrochemical Evaluation of Tumor Development via Cellular Interface Supported CRISPR/Cas Trans-Cleavage.Research (Wash D C). 2022 Apr 6;2022:9826484. doi: 10.34133/2022/9826484. eCollection 2022. Research (Wash D C). 2022. PMID: 35474904 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of a cytocidal protein from lamprey and its mechanism of action in the selective killing of cancer cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 May 27;17(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0358-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31133022 Free PMC article.
-
Sialic Acid Identity Modulates Host Tropism of Sialoglycan-binding Viridans Group Streptococci.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 26:2025.06.24.660003. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.24.660003. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Biol Chem. 2025 Jul 30:110540. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110540. PMID: 40667320 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Development and applications of sialoglycan-recognizing probes (SGRPs) with defined specificities: exploring the dynamic mammalian sialoglycome.Glycobiology. 2022 Nov 22;32(12):1116-1136. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwac050. Glycobiology. 2022. PMID: 35926090 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

