Bone Marrow Endothelial Progenitor Cells Are the Cellular Mediators of Pulmonary Hypertension in the Murine Monocrotaline Injury Model
- PMID: 28474513
- PMCID: PMC5689760
- DOI: 10.1002/sctm.16-0386
Bone Marrow Endothelial Progenitor Cells Are the Cellular Mediators of Pulmonary Hypertension in the Murine Monocrotaline Injury Model
Abstract
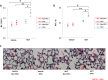
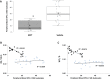
The role of bone marrow (BM) cells in modulating pulmonary hypertensive responses is not well understood. Determine if BM-derived endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) induce pulmonary hypertension (PH) and if this is attenuated by mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). Three BM populations were studied: (a) BM from vehicle and monocrotaline (MCT)-treated mice (PH induction), (b) BM from vehicle-, MCT-treated mice that received MSC-EV infusion after vehicle, MCT treatment (PH reversal, in vivo), (c) BM from vehicle-, MCT-treated mice cultured with MSC-EVs (PH reversal, in vitro). BM was separated into EPCs (sca-1+/c-kit+/VEGFR2+) and non-EPCs (sca-1-/c-kit-/VEGFR2-) and transplanted into healthy mice. Right ventricular (RV) hypertrophy was assessed by RV-to-left ventricle+septum (RV/LV+S) ratio and pulmonary vascular remodeling by blood vessel wall thickness-to-diameter (WT/D) ratio. EPCs but not non-EPCs from mice with MCT-induced PH (MCT-PH) increased RV/LV+S, WT/D ratios in healthy mice (PH induction). EPCs from MCT-PH mice treated with MSC-EVs did not increase RV/LV+S, WT/D ratios in healthy mice (PH reversal, in vivo). Similarly, EPCs from MCT-PH mice treated with MSC-EVs pre-transplantation did not increase RV/LV+S, WT/D ratios in healthy mice (PH reversal, in vitro). MSC-EV infusion reversed increases in BM-EPCs and increased lung tissue expression of EPC genes and their receptors/ligands in MCT-PH mice. These findings suggest that the pulmonary hypertensive effects of BM are mediated by EPCs and those MSC-EVs attenuate these effects. These findings provide new insights into the pathogenesis of PH and offer a potential target for development of novel PH therapies. Stem Cells Translational Medicine 2017;6:1595-1606.
Keywords: Endothelial progenitor cells; Extracellular vesicles; Mesenchymal stem cells; Monocrotaline; Pulmonary hypertension.
© 2017 The Authors Stem Cells Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Exosomes induce and reverse monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice.Cardiovasc Res. 2016 Jun 1;110(3):319-30. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw054. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Cardiovasc Res. 2016. PMID: 26980205 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of pulmonary hypertensive changes by extracellular vesicles from monocrotaline-treated mice.Cardiovasc Res. 2013 Dec 1;100(3):354-62. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt184. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Cardiovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23867631 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Marrow-Derived Endothelial Progenitor Cells Contribute to Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Rats via Inhibition of Store-Operated Ca2+ Channels.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Sep 18;2018:4892349. doi: 10.1155/2018/4892349. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30320134 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Progenitor Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Potential Therapeutic Application in Tissue Repair and Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 15;22(12):6375. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126375. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive insight into endothelial progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles as a promising candidate for disease treatment.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jun 7;13(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02921-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35672766 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New Mutations and Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Hypertension: Progress and Puzzles in Disease Pathogenesis.Circ Res. 2022 Apr 29;130(9):1365-1381. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.320084. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Circ Res. 2022. PMID: 35482831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Aldosterone on Senescence and Proliferation Inhibition of Endothelial Progenitor Cells Induced by Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Apr 18;26:e920678. doi: 10.12659/MSM.920678. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32303670 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Outgrowth and Proliferation of Endothelial Colony Forming Cells are Related to Markers of Disease Severity in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 27;19(12):3763. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123763. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30486375 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell extracellular vesicles as therapy for acute and chronic respiratory diseases: A meta-analysis.J Extracell Vesicles. 2021 Oct;10(12):e12141. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12141. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021. PMID: 34596349 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles: pathogenic messengers and potential therapy for neonatal lung diseases.Front Pediatr. 2023 Jun 16;11:1205882. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1205882. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37397144 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Montani D, Perros F, Gambaryan N et al. C‐kit‐positive cells accumulate in remodeled vessels of idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011;184:116–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

