Discovery of small molecule inhibitors of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by targeting β-catenin/Tcf4 interactions
- PMID: 28474989
- PMCID: PMC5478005
- DOI: 10.1177/1535370217708198
Discovery of small molecule inhibitors of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by targeting β-catenin/Tcf4 interactions
Abstract
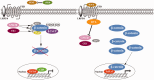
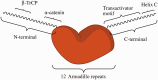
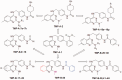
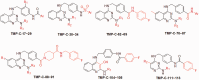
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway typically shows aberrant activation in various cancer cells, especially colorectal cancer cells. This signaling pathway regulates the expression of a variety of tumor-related proteins, including c-myc and cyclin D1, and plays essential roles in tumorigenesis and in the development of many cancers. Small molecules that block the interactions between β-catenin and Tcf4, a downstream stage of activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, could efficiently cut off this signal transduction and thereby act as a novel class of anticancer drugs. This paper reviews the currently reported inhibitors that target β-catenin/Tcf4 interactions, focusing on the discovery approaches taken in the design of these inhibitors and their bioactivities. A brief perspective is then shared on the future discovery and development of this class of inhibitors. Impact statement This mini-review summarized the current knowledge of inhibitors of interactions of beta-catenin/Tcf4 published to date according to their discovery approaches, and discussed their in vitro and in vivo activities, selectivities, and pharmacokinetic properties. Several reviews presently available now in this field describe modulators of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway, but are generally focused on the bioactivities of these inhibitors. By contrast, this review focused on the drug discovery approaches taken in identifying these types of inhibitors and provided our perspective on further strategies for future drug discoveries. This review also integrated many recently published and important works on highly selective inhibitors as well as rational drug design. We believe that the findings and strategies summarized in this review have broad implications and will be of interest throughout the biochemical and pharmaceutical research community.
Keywords: Tcf4; Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway; anticancer agents; protein–protein interactions; small molecule inhibitors; β-Catenin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure-based discovery of a novel inhibitor targeting the β-catenin/Tcf4 interaction.Biochemistry. 2012 Jan 17;51(2):724-31. doi: 10.1021/bi201428h. Epub 2012 Jan 6. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22224445
-
The β-catenin/TCF complex as a novel target of resveratrol in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Nov 1;84(9):1143-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.08.011. Epub 2012 Aug 19. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22935447
-
20(S)-ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of KG-1a cells through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2016 Jul;36(1):137-46. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4774. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27121661
-
Recent advances in β-catenin/BCL9 protein-protein interaction inhibitors.Future Med Chem. 2021 May;13(10):927-940. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2020-0357. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Future Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33849283 Review.
-
Atypical regulators of Wnt/β-catenin signaling as potential therapeutic targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Jun;242(11):1142-1149. doi: 10.1177/1535370217705865. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28429652 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Silencing TCF4 Sensitizes Melanoma Cells to Vemurafenib Through Inhibiting GLUT3-Mediated Glycolysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 29;13:4905-4915. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S245531. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32581551 Free PMC article.
-
Lupeol inhibits growth and migration in two human colorectal cancer cell lines by suppression of Wnt-β-catenin pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Nov 9;11:7987-7999. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S183925. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. Retraction in: Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Aug 20;13:8371. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S276550. PMID: 30519040 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Protein-protein interaction modulators: advances, successes and remaining challenges.Biophys Rev. 2019 Aug;11(4):559-581. doi: 10.1007/s12551-019-00570-x. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Biophys Rev. 2019. PMID: 31301019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Mechanisms of Autophagy-Targeted Antimicrobial Therapeutics Against Mycobacterial Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Mar 22;11:633360. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.633360. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33828998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An update on Wnt signaling pathway in cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Feb;9(2):1246-1252. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.12.50. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117469 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McCrea PD, Turck CW, Gumbiner B. A homolog of the armadillo protein in Drosophila (plakoglobin) associated with E-cadherin. Science 1991; 254: 1359–61. - PubMed
-
- Kemler R. From cadherins to catenins: cytoplasmic protein interactions and regulation of cell adhesion. Trends Genet 1993; 9: 317–21. - PubMed
-
- Peifer M, Rauskolb C, Williams M, Riggleman B, Wieschaus E. The segment polarity gene armadillo interacts with the wingless signaling pathway in both embryonic and adult pattern formation. Development 1991; 111: 1029–43. - PubMed
-
- Noordermeer J, Klingensmith J, Perrimon N, Nusse R. Dishevelled and armadillo act in the wingless signalling pathway in Drosophila. Nature 1994; 367: 80–3. - PubMed
-
- Holland JD, Klaus A, Garratt AN, Birchmeier W. Wnt signaling in stem and cancer stem cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2013; 25: 254–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

