Public Auditing with Privacy Protection in a Multi-User Model of Cloud-Assisted Body Sensor Networks
- PMID: 28475110
- PMCID: PMC5469637
- DOI: 10.3390/s17051032
Public Auditing with Privacy Protection in a Multi-User Model of Cloud-Assisted Body Sensor Networks
Abstract
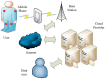
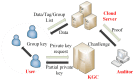
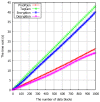
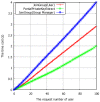
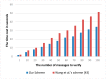
Wireless Body Sensor Networks (WBSNs) are gaining importance in the era of the Internet of Things (IoT). The modern medical system is a particular area where the WBSN techniques are being increasingly adopted for various fundamental operations. Despite such increasing deployments of WBSNs, issues such as the infancy in the size, capabilities and limited data processing capacities of the sensor devices restrain their adoption in resource-demanding applications. Though providing computing and storage supplements from cloud servers can potentially enrich the capabilities of the WBSNs devices, data security is one of the prevailing issues that affects the reliability of cloud-assisted services. Sensitive applications such as modern medical systems demand assurance of the privacy of the users' medical records stored in distant cloud servers. Since it is economically impossible to set up private cloud servers for every client, auditing data security managed in the remote servers has necessarily become an integral requirement of WBSNs' applications relying on public cloud servers. To this end, this paper proposes a novel certificateless public auditing scheme with integrated privacy protection. The multi-user model in our scheme supports groups of users to store and share data, thus exhibiting the potential for WBSNs' deployments within community environments. Furthermore, our scheme enriches user experiences by offering public verifiability, forward security mechanisms and revocation of illegal group members. Experimental evaluations demonstrate the security effectiveness of our proposed scheme under the Random Oracle Model (ROM) by outperforming existing cloud-assisted WBSN models.
Keywords: cloud computing; privacy preserving; public auditing; wireless body sensor networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Certificateless Public Auditing Scheme With Data Privacy and Dynamics in Group User Model of Cloud-Assisted Medical WSNs.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2023 May;27(5):2334-2344. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3128775. Epub 2023 May 4. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2023. PMID: 34788225
-
Public auditing for real-time medical sensor data in cloud-assisted HealthIIoT system.Front Optoelectron. 2022 Jun 29;15(1):29. doi: 10.1007/s12200-022-00028-1. Front Optoelectron. 2022. PMID: 36637558 Free PMC article.
-
Centralized Duplicate Removal Video Storage System with Privacy Preservation in IoT.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Jun 4;18(6):1814. doi: 10.3390/s18061814. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29867037 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey of Context-Aware Access Control Mechanisms for Cloud and Fog Networks: Taxonomy and Open Research Issues.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Apr 27;20(9):2464. doi: 10.3390/s20092464. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32349242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fog Computing and Edge Computing Architectures for Processing Data From Diabetes Devices Connected to the Medical Internet of Things.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017 Jul;11(4):647-652. doi: 10.1177/1932296817717007. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017. PMID: 28745086 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yick J., Mukherjee B., Ghosal D. Wireless sensor network survey. Comput. Netw. 2008;52:2292–2330. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2008.04.002. - DOI
-
- Cao H., Leung V., Chow C., Chan H. Enabling technologies for wireless body area networks: A survey and outlook. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2009;47:84–93. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2009.5350373. - DOI
-
- Chen M., Gonzalez S., Vasilakos A., Cao H., Leung V.C.M. Body area networks: A survey. Mob. Net. Appl. 2011;16:171–193. doi: 10.1007/s11036-010-0260-8. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

