Keratins regulate colonic epithelial cell differentiation through the Notch1 signalling pathway
- PMID: 28475172
- PMCID: PMC5442467
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2017.28
Keratins regulate colonic epithelial cell differentiation through the Notch1 signalling pathway
Abstract
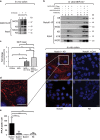
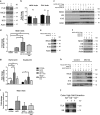
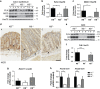
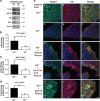
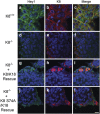
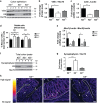
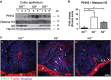
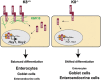
Keratins (K) are intermediate filament proteins important in stress protection and mechanical support of epithelial tissues. K8, K18 and K19 are the main colonic keratins, and K8-knockout (K8-/-) mice display a keratin dose-dependent hyperproliferation of colonic crypts and a colitis-phenotype. However, the impact of the loss of K8 on intestinal cell differentiation has so far been unknown. Here we show that K8 regulates Notch1 signalling activity and differentiation in the epithelium of the large intestine. Proximity ligation and immunoprecipitation assays demonstrate that K8 and Notch1 co-localize and interact in cell cultures, and in vivo in the colonic epithelial cells. K8 with its heteropolymeric partner K18 enhance Notch1 protein levels and activity in a dose dependent manner. The levels of the full-length Notch1 receptor (FLN), the Notch1 intracellular domain (NICD) and expression of Notch1 downstream target genes are reduced in the absence of K8, and the K8-dependent loss of Notch1 activity can be rescued with re-expression of K8/K18 in K8-knockout CRISPR/Cas9 Caco-2 cells protein levels. In vivo, K8 deletion with subsequent Notch1 downregulation leads to a shift in differentiation towards a goblet cell and enteroendocrine phenotype from an enterocyte cell fate. Furthermore, the K8-/- colonic hyperproliferation results from an increased number of transit amplifying progenitor cells in these mice. K8/K18 thus interact with Notch1 and regulate Notch1 signalling activity during differentiation of the colonic epithelium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The amount of keratins matters for stress protection of the colonic epithelium.PLoS One. 2015 May 22;10(5):e0127436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127436. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26000979 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of keratins 8 and 18 in rodent epithelial cell lines associates with keratin gene mutation and DNA methylation: Cell line selective effects on cell invasion.Exp Cell Res. 2015 Jul 1;335(1):12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.04.003. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Exp Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25882495 Free PMC article.
-
Defining a timeline of colon pathologies after keratin 8 loss: rapid crypt elongation and diarrhea are followed by epithelial erosion and cell exfoliation.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024 Jan 1;326(1):G67-G77. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00140.2023. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024. PMID: 37962942 Free PMC article.
-
Keratins let liver live: Mutations predispose to liver disease and crosslinking generates Mallory-Denk bodies.Hepatology. 2007 Nov;46(5):1639-49. doi: 10.1002/hep.21976. Hepatology. 2007. PMID: 17969036 Review.
-
Revealing the Roles of Keratin 8/18-Associated Signaling Proteins Involved in the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 15;22(12):6401. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126401. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203895 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted deletion of keratin 8 in intestinal epithelial cells disrupts tissue integrity and predisposes to tumorigenesis in the colon.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec 24;79(1):10. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04081-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34951664 Free PMC article.
-
Colonocyte keratins stabilize mitochondria and contribute to mitochondrial energy metabolism.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024 Sep 1;327(3):G438-G453. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00220.2023. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38860856
-
Chemosensitivity analysis and study of gene resistance on tumors and cancer stem cell isolates from patients with colorectal cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Oct;24(4):721. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12360. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34396431 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of cytokeratin 8 overcomes chemoresistance of chordoma cells by aggravating endoplasmic reticulum stress through PERK/eIF2α arm of unfolded protein response and blocking autophagy.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Nov 25;10(12):887. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2125-9. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31767864 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of epithelial transitional states in murine and human pulmonary fibrosis.J Clin Invest. 2023 Nov 15;133(22):e165612. doi: 10.1172/JCI165612. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37768734 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

