CD69: from activation marker to metabolic gatekeeper
- PMID: 28475283
- PMCID: PMC6485631
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201646837
CD69: from activation marker to metabolic gatekeeper
Abstract
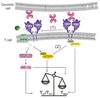
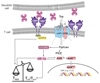
CD69 is a membrane-bound, type II C-lectin receptor. It is a classical early marker of lymphocyte activation due to its rapid appearance on the surface of the plasma membrane after stimulation. CD69 is expressed by several subsets of tissue resident immune cells, including resident memory T (TRM) cells and gamma delta (γδ) T cells, and is therefore considered a marker of tissue retention. Recent evidence has revealed that CD69 regulates some specific functions of selected T-cell subsets, determining the migration-retention ratio as well as the acquisition of effector or regulatory phenotypes. Specifically, CD69 regulates the differentiation of regulatory T (Treg) cells as well as the secretion of IFN-γ, IL-17, and IL-22. The identification of putative CD69 ligands, such as Galectin-1 (Gal-1), suggests that CD69-induced signaling can be regulated not only during cognate contacts between T cells and antigen-presenting cells in lymphoid organs, but also in the periphery, where cytokines and other metabolites control the final outcome of the immune response. Here, we will discuss new aspects of the molecular signaling mediated by CD69 and its involvement in the metabolic reprogramming regulating TH-effector lineages.
Keywords: CD69; Galectin-1; LAT1; Metabolism; S1P1; T cells; mTOR.
© 2017 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest
Figures
References
-
- Ziegler SF, Ramsdell F, Hjerrild KA, Armitage RJ, Grabstein KH, Hennen KB, Farrah T, et al. Molecular characterization of the early activation antigen CD69: a type II membrane glycoprotein related to a family of natural killer cell activation antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1993;23:1643–1648. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Cabrera M, Santis AG, Fernandez-Ruiz E, Blacher R, Esch F, Sanchez-Mateos P, Sanchez-Madrid F. Molecular cloning, expression, and chromosomal localization of the human earliest lymphocyte activation antigen AIM/CD69, a new member of the C-type animal lectin superfamily of signal-transmitting receptors. J Exp Med. 1993;178:537–547. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Cabrera M, Munoz E, Blazquez MV, Ursa MA, Santis AG, Sanchez-Madrid F. Transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding the human C-type lectin leukocyte receptor AIM/CD69 and functional characterization of its tumor necrosis factor-alpha-responsive elements. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:21545–21551. - PubMed
-
- Castellanos MC, Munoz C, Montoya MC, Lara-Pezzi E, Lopez-Cabrera M, de Landazuri MO. Expression of the leukocyte early activation antigen CD69 is regulated by the transcription factor AP-1. J Immunol. 1997;159:5463–5473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

