Isomeric Separation of Permethylated Glycans by Porous Graphitic Carbon (PGC)-LC-MS/MS at High Temperatures
- PMID: 28475308
- PMCID: PMC5761069
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00747
Isomeric Separation of Permethylated Glycans by Porous Graphitic Carbon (PGC)-LC-MS/MS at High Temperatures
Abstract
Permethylation is a common derivatization method for MS-based glycomic analyses. Permethylation enhances glycan ionization efficiency in positive MS analysis and improves glycan structural stability. Recent biological glycomic studies have added to the growing body of knowledge and suggest the need for complete structural analysis of glycans. However, reverse phase LC analysis of permethylated glycans usually results in poor isomeric separation. To achieve isomeric separation of permethylated glycans, a porous graphitic carbon (PGC) column was used. PGC columns are well-known for their isomeric separation capability for hydrophilic analyses. In this study, we have optimized temperature conditions to overcome the issues encountered while separating permethylated glycans on a PGC column and found that the highest temperature examined, 75 °C, was optimal. Additionally, we utilized tandem MS to elucidate detailed structural information for the isomers separated. Glycan standards were also utilized to facilitate structural identifications through MS/MS spectra and retention time comparison. The result is an efficient and sensitive method capable of the isomeric separation of permethylated glycans. This method was successfully applied for the isomeric characterization of N-glycans released from the breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-231BR (brain seeking). A total of 127 unique glycan structures were identified with 39 isobaric structures, represented as 106 isomers, with 21 nonisomeric glycans. Thirty seven structures exhibited significant differences in isomeric distribution (P < 0.05). Additionally, alterations in the distribution of isomeric sialylated glycans, structures known to be involved in cell attachment to the blood-brain barrier during brain metastasis, were observed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
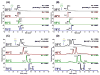
 , N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc);
, N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc);
 , Galactose (Gal);
, Galactose (Gal);
 , Fucose (Fuc);
, Fucose (Fuc);
 , Mannose (Man);
, Mannose (Man);
 , N-acetylneuraminic acid (NeuAc/Sialic Acid)
, N-acetylneuraminic acid (NeuAc/Sialic Acid)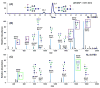


Similar articles
-
LC-MS/MS analysis of permethylated N-glycans facilitating isomeric characterization.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017 Jan;409(2):453-466. doi: 10.1007/s00216-016-9996-8. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017. PMID: 27796453 Free PMC article.
-
Isomeric separation of permethylated glycans by extra-long reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPLC)-MS/MS.Analyst. 2022 May 17;147(10):2048-2059. doi: 10.1039/d2an00010e. Analyst. 2022. PMID: 35311852 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS isomeric profiling of permethylated N-glycans derived from serum haptoglobin of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and cirrhotic patients.Electrophoresis. 2017 Sep;38(17):2160-2167. doi: 10.1002/elps.201700025. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Electrophoresis. 2017. PMID: 28543513 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of isomeric glycan structures by LC-MS/MS.Electrophoresis. 2017 Sep;38(17):2100-2114. doi: 10.1002/elps.201700042. Epub 2017 May 17. Electrophoresis. 2017. PMID: 28370073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Applications of chromatography in glycomics].Se Pu. 2024 Jul;42(7):646-657. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2023.12003. Se Pu. 2024. PMID: 38966973 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Accurate Identification of Isomeric Glycans by Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry-Electronic Excitation Dissociation Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2020 Oct 6;92(19):13211-13220. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02374. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Anal Chem. 2020. PMID: 32865981 Free PMC article.
-
Multistage Ion Mobility Spectrometry Combined with Infrared Spectroscopy for Glycan Analysis.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2023 Apr 5;34(4):695-700. doi: 10.1021/jasms.2c00361. Epub 2023 Mar 7. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2023. PMID: 36881006 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Classifies Core and Outer Fucosylation of N-Glycoproteins Using Mass Spectrometry.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 15;10(1):318. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-57274-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31941975 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative clinical glycomics strategies: A guide for selecting the best analysis approach.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2022 Nov;41(6):901-921. doi: 10.1002/mas.21688. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2022. PMID: 33565652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon Nanoparticles and Graphene Nanosheets as MALDI Matrices in Glycomics: a New Approach to Improve Glycan Profiling in Biological Samples.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2018 Sep;29(9):1892-1900. doi: 10.1007/s13361-018-1985-z. Epub 2018 Jun 18. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2018. PMID: 29916086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freeze HH, Esko JD, Parodi AJ. Essentials of Glycobiology. Cold Spring Harbor (NY): 2009. - PubMed
-
- Molinari M. Nat Chem Biol. 2007;3:313–320. - PubMed
-
- Varki A, Kannagi R, Toole BP. Essentials of Glycobiology. Cold Spring Harbor (NY): 2009.
-
- Ciucanu IKF. Carbohydr Res. 1984;131:209–217.
-
- Kang P, Mechref Y, Novotny MV. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2008;22:721–734. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

