RIG-I-Like Receptors and Type I Interferonopathies
- PMID: 28475461
- PMCID: PMC5439449
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2016.0095
RIG-I-Like Receptors and Type I Interferonopathies
Abstract
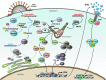
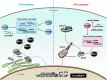
Type I interferon (IFN) production by the proper activation of nucleic acid sensors is essential for hosts to eliminate invading viruses. Among these sensors, RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) are well-known viral RNA sensors in the cytoplasm that recognize the nonself signatures of viral RNAs to trigger IFN responses. Recent accumulating evidence has clarified that some specific and atypical self-RNAs also cause activation of RLRs independently of virus infection. Importantly, when RLR-activation by these RNAs or a conformational change via missense mutations is sustained, the resulting continuous production of type I IFN will lead to autoimmune disorders. We, herein, focus on autoimmune diseases caused by chronic activation of RLRs and discuss possible mechanisms of their onset.
Keywords: RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs); autoimmune diseases; interferon (IFN).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Ablasser A, Hemmerling I, Schmid-Burgk JL, Behrendt R, Roers A, Hornung V. 2014. TREX1 deficiency triggers cell-autonomous immunity in a cGAS-dependent manner. J Immunol 192(12):5993–5997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

