Betulinic acid protects against N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced redox imbalance in testes of rats
- PMID: 28475470
- PMCID: PMC8900629
- DOI: 10.1080/13510002.2017.1322750
Betulinic acid protects against N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced redox imbalance in testes of rats
Abstract
Objectives: N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) is known to elicit carcinogenic activity in the liver and kidney of animals. There is a dearth of information of its effect in testis. This study evaluated the protective role of betulinic acid (BA) against NDMA-induced redox imbalance in testes of rats.
Methodology: Twenty-four male rats were assigned into four groups and treated with normal saline, BA, NDMA and [BA+NDMA]. BA (25 mg/kg) was given for 14 days, while NDMA (5 mg/kg) was given on days 7 and 12.
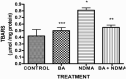
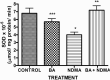
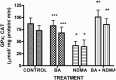
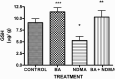
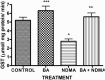
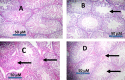
Results: Administration of NDMA significantly increased the weight and relative weight of testes by 51 and 71%, respectively, while treatment with BA attenuated the weight-gain. Furthermore, NDMA decreased the sperm count, motility and live-dead ratio by 57, 36 and 37%, respectively, and increased total sperm abnormality by 56%. However, BA attenuated the changes in the spermiogram of NDMA-treated rats. NDMA significantly decreased the activities of antioxidative enzymes, follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, while testicular levels of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances and total cholesterol were increased. Also, NDMA increased the activities of aniline hydroxylase and aminopyrine-N-demethylase. Supplementation with BA attenuated NDMA-induced alteration in these biochemical indices.
Conclusion: BA protects against NDMA-induced redox imbalance via activation of antioxidative pathway.
Keywords: Sperm quality; antioxidant; oxidative stress; phase I and II enzymes; toxicant.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Betulinic Acid Attenuates T-2-Toxin-Induced Testis Oxidative Damage Through Regulation of the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Mice.Biomolecules. 2019 Nov 26;9(12):787. doi: 10.3390/biom9120787. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31779213 Free PMC article.
-
Betulinic acid abates N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced changes in lipid metabolism, oxidative stress, and inflammation in the liver and kidney of Wistar rats.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021 Nov;35(11):e22901. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22901. Epub 2021 Sep 2. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34472159
-
Modulatory role of betulinic acid in N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced hepatorenal toxicity in male Wistar rats.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2017 Jul;36(7):734-743. doi: 10.1177/0960327116661399. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27492479
-
Interactions of betulinic acid with xenobiotic metabolizing and antioxidative enzymes in DMBA-treated Sprague Dawley female rats.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:131-142. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.06.016. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23777707
-
Protective effects of Artocarpus altilis (Moraceae) on cadmium-induced changes in sperm characteristics and testicular oxidative damage in rats.Andrologia. 2016 Mar;48(2):152-63. doi: 10.1111/and.12426. Epub 2015 Apr 25. Andrologia. 2016. PMID: 25912632
Cited by
-
Selective hepatitis B and D virus entry inhibitors from the group of pentacyclic lupane-type betulin-derived triterpenoids.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 10;10(1):21772. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78618-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33303817 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of Crocin on sperm parameters disorders induced by peripheral administration of nitrosamines in male rats.J Med Life. 2022 Mar;15(3):362-367. doi: 10.25122/jml-2019-0144. J Med Life. 2022. PMID: 35450005 Free PMC article.
-
Reproductive and developmental toxicology of nitrosamines.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025 Apr 16;14(2):tfaf051. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaf051. eCollection 2025 Apr. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40248818 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of N-nitrosodimethylamine induced hepatic fibrosis.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jan 8;10(1):18. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1272-8. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30622238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Betulinic Acid Attenuates T-2-Toxin-Induced Testis Oxidative Damage Through Regulation of the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Mice.Biomolecules. 2019 Nov 26;9(12):787. doi: 10.3390/biom9120787. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31779213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herrmann SS, Deudahl-Olesen L, Granby K. Occurrence of volatile and non-volatile N-nitrosamines in processed meat products and role of heat treatment. Food Control. 2015;48:163–169. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.05.030 - DOI
-
- Ortiz de Montellano PR, De Voss JJ. Cytochrome P450: structure, mechanism, and biochemistry. 3rd ed. Ortiz de Montellano PR, editor. New York (NY: ): Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers; 2005. p. 183–245.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
