Efficacy of NH3 as a secondary barrier treatment for inactivation of Salmonella Typhimurium and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in digestate of animal carcasses: Proof-of-concept
- PMID: 28475586
- PMCID: PMC5419515
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176825
Efficacy of NH3 as a secondary barrier treatment for inactivation of Salmonella Typhimurium and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in digestate of animal carcasses: Proof-of-concept
Abstract
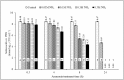
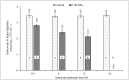
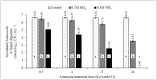
Managing the disposal of infectious animal carcasses from routine and catastrophic disease outbreaks is a global concern. Recent research suggests that burial in lined and aerated trenches provides the rapid pathogen containment provided by burial, while reducing air and water pollution potential and the length of time that land is taken out of agricultural production. Survival of pathogens in the digestate remains a concern, however. A potential answer is a 'dual'-barrier approach in which ammonia is used as a secondary barrier treatment to reduce the risk of pathogen contamination when trench liners ultimately leak. Results of this study showed that the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of NH3 is 0.1 M (~1,468 NH3-N mg/L), and 0.5 M NH3 (~7,340 NH3-N mg/L) for ST4232 & MRSA43300, respectively at 24 h and pH = 9±0.1 and inactivation was increased by increasing NH3 concentration and/or treatment time. Results for digestate treated with NH3 were consistent with the MICs, and both pathogens were completely inactivated within 24 h.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Sparks Companies Inc. 2002. Livestock Mortalities: Methods of Disposal and Their Potential Costs. Report for the National Renderers Association, Alexandria, VA. http://assets.nationalrenderers.org/mortalities_final.pdf.
-
- Nutsch A, Kastner J. Carcass Disposal Options, In: Voeller JG (ed), Wiley Handbook of Science and Technology for Homeland Security. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2010. Hoboken, NJ: p. 1959.
-
- Huong VT, Thanh LV, Phu VD, Trinh DT, Inui K, Tung N, et al. Temporal and spatial association of Streptococcus suis infection in humans and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome outbreaks in pigs in northern Vietnam. Epidemiology and Infection. 2016;144(1): 35–44. 10.1017/S0950268815000990. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

