Activation of Akt characterizes estrogen receptor positive human breast cancers which respond to anthracyclines
- PMID: 28476032
- PMCID: PMC5522318
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17167
Activation of Akt characterizes estrogen receptor positive human breast cancers which respond to anthracyclines
Abstract
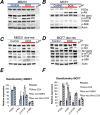
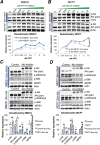
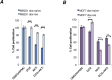
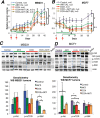
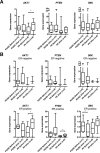
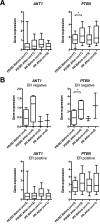
Anthracyclines are key components of human breast cancer chemotherapy. Here, we explored the role of Akt signaling in anthracycline resistance.The antitumor activity of doxorubicin and Akt inhibitor A-443654 alone or combined was examined in estrogen receptor (ER) positive and negative human breast cancer cell lines. Further, we examined mRNA changes induced by anthracyclines in locally advanced breast cancers biopsied before and after treatment in two clinical trials.Doxorubicin increased Akt phosphorylation in ER positive MCF7 and T47D cell lines, with no effect in ER negative MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells. A-443654 was significantly more cytotoxic in doxorubicin-resistant compared to doxorubicin-naïve MCF7. This difference was not observed in MDA-MB231. Among 24 patients, AKT1 gene expression increased 24 hrs after the initial epirubicin exposure in ER positive tumors responding to therapy (n=6), as compared to ER positive non-responders (n=7) or ER negative tumors (n=11). In contrast, AKT1 mRNA changes after 16 weeks of doxorubicin were unrelated to clinical response and ER status (n=30).In conclusion, rapid Akt activation was observed in ER positive breast cancers which responded to anthracyclines. Increased cytotoxicity of A-443654 in doxorubicin-resistant MCF7 cells indicates a possible role for Akt inhibitors in ER positive breast cancers where chemoresistance evolves.
Keywords: Akt; breast cancer; doxorubicin; drug resistance; estrogen receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tamoxifen resistance alters sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in a subset of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 8;16(6):e0252822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252822. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34101751 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of resveratrol on doxorubicin resistance in breast neoplasm cells by modulating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.IUBMB Life. 2018 Jun;70(6):491-500. doi: 10.1002/iub.1749. Epub 2018 Apr 10. IUBMB Life. 2018. PMID: 29637742
-
Alterations in estrogen signalling pathways upon acquisition of anthracycline resistance in breast tumor cells.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 14;12(2):e0172244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172244. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28196134 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterization of aromatase, estrogen receptor, and their genes in endocrine-responsive and -resistant breast cancer cells.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Jul;161:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.07.018. Epub 2015 Aug 13. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26277097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Doxorubicin and other anthracyclines in cancers: Activity, chemoresistance and its overcoming.Mol Aspects Med. 2023 Oct;93:101205. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2023.101205. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Mol Aspects Med. 2023. PMID: 37515939 Review.
Cited by
-
Enzalutamide-induced signatures revealed by epigenetic plasticity using single-cell multi-omics sequencing in prostate cancer.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Feb 18;31:648-661. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.02.022. eCollection 2023 Mar 14. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023. PMID: 36910711 Free PMC article.
-
Vav1 downmodulates Akt in different breast cancer subtypes: a new promising chance to improve breast cancer outcome.Mol Oncol. 2018 Jun;12(7):1012-1025. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12203. Epub 2018 May 16. Mol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29658179 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Targeting of Estrogen Receptor Alpha and XPO1 Prevent Akt Activation, Remodel Metabolic Pathways and Induce Autophagy to Overcome Tamoxifen Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Apr 4;11(4):479. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040479. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30987380 Free PMC article.
-
Meta analysis of bioactive compounds, miRNA, siRNA and cell death regulators as sensitizers to doxorubicin induced chemoresistance.Apoptosis. 2022 Oct;27(9-10):622-646. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01742-z. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Apoptosis. 2022. PMID: 35716277 Review.
-
Chemoresistant tumor cell secretome potentiates immune suppression in triple negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 14;27(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s13058-025-02082-x. Breast Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40660361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baselga J. Targeting the phosphoinositide-3 (PI3) kinase pathway in breast cancer. Oncologist. 2011;16(Suppl 1):12–19. - PubMed
-
- Nagata Y, Lan KH, Zhou X, Tan M, Esteva FJ, Sahin AA, Klos KS, Li P, Monia BP, Nguyen NT, Hortobagyi GN, Hung MC, Yu D. PTEN activation contributes to tumor inhibition by trastuzumab, and loss of PTEN predicts trastuzumab resistance in patients. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:117–127. - PubMed
-
- Hurvitz SA, Andre F, Jiang Z, Shao Z, Mano MS, Neciosup SP, Tseng LM, Zhang Q, Shen K, Liu D, Dreosti LM, Burris HA, Toi M, et al. Combination of everolimus with trastuzumab plus paclitaxel as first-line treatment for patients with HER2-positive advanced breast cancer (BOLERO-1): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:816–829. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

