Impaired Corneal Sensation and Nerve Loss in a Type 2 Rat Model of Chronic Diabetes Is Reversible With Combination Therapy of Menhaden Oil, α-Lipoic Acid, and Enalapril
- PMID: 28476051
- PMCID: PMC5421399
- DOI: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000001182
Impaired Corneal Sensation and Nerve Loss in a Type 2 Rat Model of Chronic Diabetes Is Reversible With Combination Therapy of Menhaden Oil, α-Lipoic Acid, and Enalapril
Abstract
Purpose: This study investigated the efficacy of monotherapy versus combination of menhaden oil, α-lipoic acid, and enalapril on corneal sensation and morphometry and other neuropathy-related endpoints in a rat model of type 2 diabetes.
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (aged 12 weeks) were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks followed by 30 mg/kg streptozotocin. After 16 weeks of hyperglycemia, 12-week treatments consisting of menhaden oil, α-lipoic acid, enalapril, or their combination were initiated. Before and after treatments, we performed analyses of multiple neural and vascular endpoints including corneal sensitivity, corneal nerve density, vascular reactivity of epineurial arterioles, motor and sensory nerve conduction velocity, intraepidermal nerve fiber density, and thermal nociception.
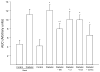
Results: Before treatment, all the neural and vascular endpoints in diabetic rats were impaired. Treating diabetic rats with monotherapy was effective in improving neural and vascular deficits with menhaden oil being most efficacious. However, the combination therapy provided the greatest benefit and improved/reversed all nerve and vascular deficits. The effect of combination therapy on corneal relative sensitivity and structure (in mm/mm), primary endpoints for this study, for control, diabetic, and diabetic treated rats was 4.2 ± 1.4 and 7.5 ± 0.5, 12.1 ± 1.3* and 3.8 ± 0.2*, and 6.6 ± 2.3 and 7.3 ± 0.5, respectively (*P < 0.05 compared with control rats; P < 0.05 compared with diabetic rats).
Conclusions: These studies suggest that a combination therapeutic approach may be most effective for treating vascular and neural complications of type 2 diabetes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of combination therapy consisting of enalapril, α-lipoic acid, and menhaden oil on diabetic neuropathy in a high fat/low dose streptozotocin treated rat.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 15;765:258-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.08.015. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26291662
-
Early vs. late intervention of high fat/low dose streptozotocin treated C57Bl/6J mice with enalapril, α-lipoic acid, menhaden oil or their combination: Effect on diabetic neuropathy related endpoints.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Apr;116:122-131. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.12.022. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28025096 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme and/or neutral endopeptidase on vascular and neural complications in high fat fed/low dose streptozotocin-diabetic rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Feb 29;677(1-3):180-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.12.003. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22198047 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of prostaglandin E1 plus lipoic acid combination therapy versus monotherapy for patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy.J Clin Neurosci. 2016 May;27:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2015.07.028. Epub 2016 Feb 3. J Clin Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26775115 Review.
-
The impact of diabetes on corneal nerve morphology and ocular surface integrity.Ocul Surf. 2018 Jan;16(1):45-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2017.10.006. Epub 2017 Nov 4. Ocul Surf. 2018. PMID: 29113918 Review.
Cited by
-
Animal Models in Eye Research: Focus on Corneal Pathologies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 23;24(23):16661. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316661. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38068983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetic Corneal Neuropathy: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 23;13:816062. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.816062. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35281903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progressive Loss of Corneal Nerve Fibers and Sensitivity in Rats Modeling Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Is Reversible with Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intervention: Supporting Cornea Analyses as a Marker for Peripheral Neuropathy and Treatment.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Apr 24;13:1367-1384. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S247571. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 32425569 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dietary oils on peripheral neuropathy-related endpoints in dietary obese rats.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2018 Apr 9;11:117-127. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S159071. eCollection 2018. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2018. PMID: 29674850 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: What have we Learned from Animal Models?Curr Diabetes Rev. 2022;18(5):e040521193121. doi: 10.2174/1573399817666210504101609. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2022. PMID: 33949936 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Davidson EP, Holmes A, Coppey LJ, et al. Effect of combination therapy consisting of enalapril, α-lipoic acid, and menhaden oil on diabetic neuropathy in a high fat/low dose streptozotocin treated rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;765:258–267. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

