Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibition with linagliptin reduces western diet-induced myocardial TRAF3IP2 expression, inflammation and fibrosis in female mice
- PMID: 28476142
- PMCID: PMC5420102
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-017-0544-4
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibition with linagliptin reduces western diet-induced myocardial TRAF3IP2 expression, inflammation and fibrosis in female mice
Abstract
Background: Diastolic dysfunction (DD), a hallmark of obesity and primary defect in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, is a predictor of future cardiovascular events. We previously reported that linagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, improved DD in Zucker Obese rats, a genetic model of obesity and hypertension. Here we investigated the cardioprotective effects of linagliptin on development of DD in western diet (WD)-fed mice, a clinically relevant model of overnutrition and activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Methods: Female C56Bl/6 J mice were fed an obesogenic WD high in fat and simple sugars, and supplemented or not with linagliptin for 16 weeks.
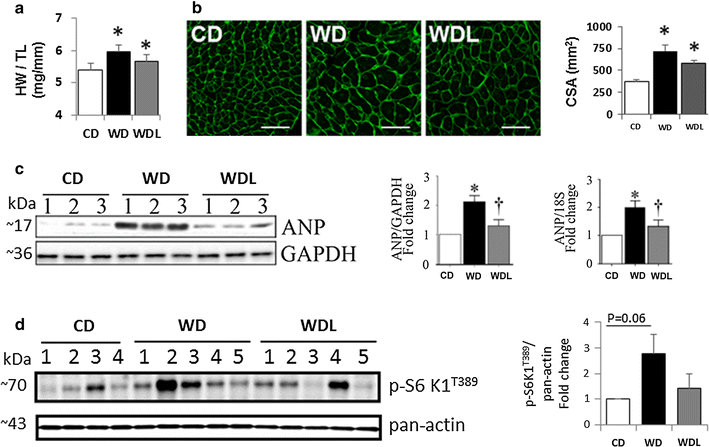
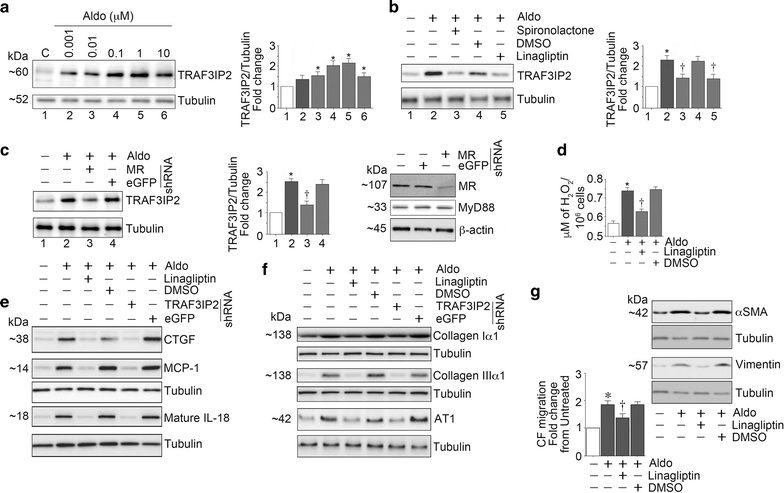
Results: WD induced oxidative stress, inflammation, upregulation of Angiotensin II type 1 receptor and mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) expression, interstitial fibrosis, ultrastructural abnormalities and DD. Linagliptin inhibited cardiac DPP-4 activity and prevented molecular impairments and associated functional and structural abnormalities. Further, WD upregulated the expression of TRAF3IP2, a cytoplasmic adapter molecule and a regulator of multiple inflammatory mediators. Linagliptin inhibited its expression, activation of its downstream signaling intermediates NF-κB, AP-1 and p38-MAPK, and induction of multiple inflammatory mediators and growth factors that are known to contribute to development and progression of hypertrophy, fibrosis and contractile dysfunction. Linagliptin also inhibited WD-induced collagens I and III expression. Supporting these in vivo observations, linagliptin inhibited aldosterone-mediated MR-dependent oxidative stress, upregulation of TRAF3IP2, proinflammatory cytokine, and growth factor expression, and collagen induction in cultured primary cardiac fibroblasts. More importantly, linagliptin inhibited aldosterone-induced fibroblast activation and migration.
Conclusions: Together, these in vivo and in vitro results suggest that inhibition of DPP-4 activity by linagliptin reverses WD-induced DD, possibly by targeting TRAF3IP2 expression and its downstream inflammatory signaling.
Keywords: Diastolic dysfunction; Linagliptin; Myocardial fibrosis; Obesity; TRAF3IP2.
Figures








References
-
- Peterson LR, Waggoner AD, Schechtman KB, Meyer T, Gropler RJ, Barzilai B, Davila-Roman VG. Alterations in left ventricular structure and function in young healthy obese women: assessment by echocardiography and tissue doppler imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(8):1399–1404. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2003.10.062. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Peterson LR, Saeed IM, McGill JB, Herrero P, Schechtman KB, Gunawardena R, Recklein CL, Coggan AR, Demoss AJ, Dence CS, et al. Sex and type 2 diabetes: obesity-independent effects on left ventricular substrate metabolism and relaxation in humans. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2012;20(4):802–810. doi: 10.1038/oby.2011.208. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

