Dioxins and related environmental contaminants increase TDP-43 levels
- PMID: 28476168
- PMCID: PMC5420162
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-017-0177-9
Dioxins and related environmental contaminants increase TDP-43 levels
Abstract
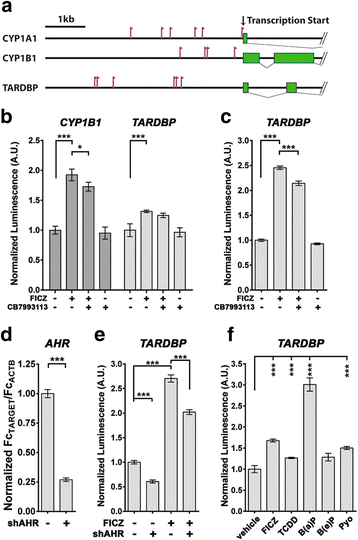
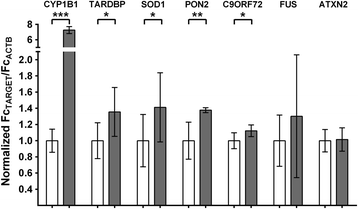
Background: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a debilitating neurodegenerative condition that is characterized by progressive loss of motor neurons and the accumulation of aggregated TAR DNA Binding Protein-43 (TDP-43, gene: TARDBP). Increasing evidence indicates that environmental factors contribute to the risk of ALS. Dioxins, related planar polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are environmental contaminants that activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), a ligand-activated, PAS family transcription factor. Recently, exposure to these toxicants was identified as a risk factor for ALS.
Methods: We examined levels of TDP-43 reporter activity, transcript and protein. Quantification was done using cell lines, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and mouse brain. The target samples were treated with AHR agonists, including 6-Formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ, a potential endogenous ligand, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo(p)dioxin, and benzo(a)pyrene, an abundant carcinogen in cigarette smoke). The action of the agonists was inhibited by concomitant addition of AHR antagonists or by AHR-specific shRNA.
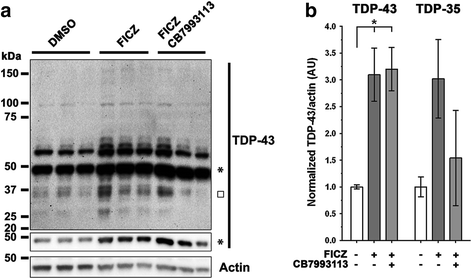
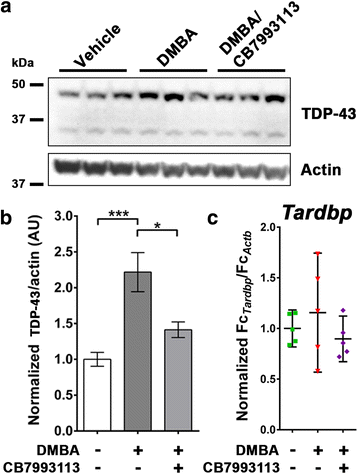
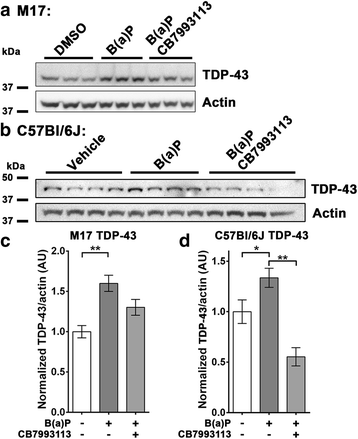
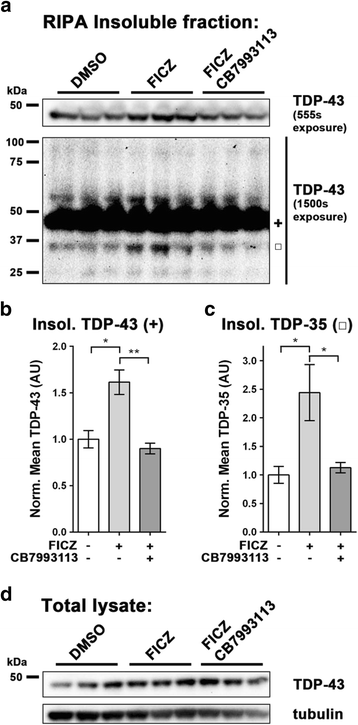
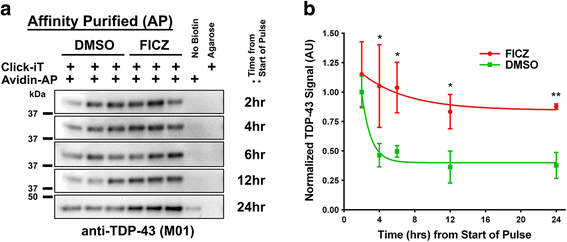
Results: We now report that AHR agonists induce up to a 3-fold increase in TDP-43 protein in human neuronal cell lines (BE-M17 cells), motor neuron differentiated iPSCs, and in murine brain. Chronic treatment with AHR agonists elicits over 2-fold accumulation of soluble and insoluble TDP-43, primarily because of reduced TDP-43 catabolism. AHR antagonists or AHR knockdown inhibits agonist-induced increases in TDP-43 protein and TARDBP transcription demonstrating that the ligands act through the AHR.
Conclusions: These results provide the first evidence that environmental AHR ligands increase TDP-43, which is the principle pathological protein associated with ALS. These results suggest novel molecular mechanisms through which a variety of prevalent environmental factors might directly contribute to ALS. The widespread distribution of dioxins, PCBs and PAHs is considered to be a risk factor for cancer and autoimmune diseases, but could also be a significant public health concern for ALS.
Keywords: ALS; Alpha-synuclein; Ataxin-2; Fus; Gene regulation; Neurodegeneration; Promoter; Protein aggregation; Toxicants; Transcription.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of CC-chemokine ligand 5 by aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands.J Dermatol Sci. 2013 Oct;72(1):9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.04.031. Epub 2013 Jun 13. J Dermatol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23810773
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated activity of mutagenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons determined using in vitro reporter gene assay.Mutat Res. 2001 Oct 18;497(1-2):49-62. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5718(01)00240-6. Mutat Res. 2001. PMID: 11525907
-
Changes in toxicity and Ah receptor agonist activity of suspended particulate matter during flood events at the rivers Neckar and Rhine - a mass balance approach using in vitro methods and chemical analysis.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2008 Oct;15(7):536-53. doi: 10.1007/s11356-008-0056-6. Epub 2008 Oct 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2008. PMID: 18936997
-
From TCDD-mediated toxicity to searches of physiologic AHR functions.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;155:419-424. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.07.032. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30055148 Review.
-
[The involvement and underlying mechanism of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in the impairment of male mammalian fertility induced by environmental pollutants].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024 Aug 25;76(4):631-642. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39192795 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Autoimmunity and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: From Laboratory Study to Clinical Practice.Clin Interv Aging. 2023 Mar 27;18:495-503. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S394286. eCollection 2023. Clin Interv Aging. 2023. PMID: 37008802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental risk scores of persistent organic pollutants associate with higher ALS risk and shorter survival in a new Michigan case/control cohort.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 14;95(3):241-248. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2023-332121. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 37758454 Free PMC article.
-
Heavy Metal Neurotoxicants Induce ALS-Linked TDP-43 Pathology.Toxicol Sci. 2019 Jan 1;167(1):105-115. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy267. Toxicol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30371865 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Oxidative Stress as a Double Agent and Its Biological and Therapeutic Significance.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 16;23(12):6719. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126719. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Airborne lead and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) risk in the U.S.Sci Total Environ. 2022 May 1;819:153096. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153096. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 35041949 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

