Murine model and mechanisms of treatment-induced painful diabetic neuropathy
- PMID: 28476321
- PMCID: PMC5501289
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.04.036
Murine model and mechanisms of treatment-induced painful diabetic neuropathy
Abstract
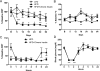
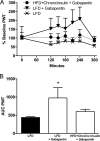
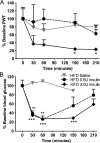
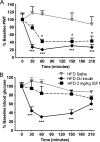
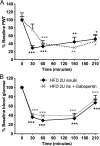
Diabetes mellitus represents a group of metabolic diseases that are characterized by hyperglycemia caused by either lack of insulin production or a reduced ability to respond to insulin. It is estimated that there were 347 million people worldwide who suffered from diabetes in 2008 and incidence is predicted to double by 2050. Neuropathy is the most common complication of long-term diabetes and approximately 30% of these subjects develop chronic neuropathic pain. A distinct acute, severe form of neuropathic pain, called insulin neuritis or treatment-induced painful neuropathy of diabetes (TIND), may also occur shortly after initiation of intensive glycemic control, with an incidence rate of up to 10.9%. The pathological mechanisms leading to TIND, which is mostly unresponsive to analgesics, are not yet understood, impeding the development of therapies. Studies to date have been clinical and with limited cohorts of patients. In the current study, we developed chronic and acute insulin-induced neuropathic pain in mice with type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes. Furthermore, we determined that insulin-induced acute allodynia is independent of glycemia levels, can also be induced with Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF1) and be prevented by inhibition of AKT, providing evidence of an insulin/IGF1 signaling pathway-based mechanism for TIND. This mouse model is useful for the elucidation of mechanisms contributing to TIND and for the testing of new therapeutic approaches to treat TIND.
Keywords: TIND; diabetes; insulin; insulin neuritis; neuropathy.
Copyright © 2017 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Albers JW, Herman WH, Pop-Busui R, Feldman EL, Martin CL, Cleary PA, Waberski BH, Lachin JM, Diabetes C Complications Trial /Epidemiology of Diabetes I, Complications Research G. Effect of prior intensive insulin treatment during the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) on peripheral neuropathy in type 1 diabetes during the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) Study. Diabetes care. 2010;33:1090–1096. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Apfel SC. Neurotrophic factors in the therapy of diabetic neuropathy. Am J Med. 1999;107:34S–42S. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

