Outcomes Over 90-Day Episodes of Care in Medicare Fee-for-Service Beneficiaries Receiving Joint Arthroplasty
- PMID: 28476495
- PMCID: PMC5572486
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arth.2017.03.040
Outcomes Over 90-Day Episodes of Care in Medicare Fee-for-Service Beneficiaries Receiving Joint Arthroplasty
Abstract
Background: In an effort to improve quality and reduce costs, payments are being increasingly tied to value through alternative payment models, such as episode-based payments. The objective of this study was to better understand the pattern and variation in outcomes among Medicare beneficiaries receiving lower extremity joint arthroplasty over 90-day episodes of care.
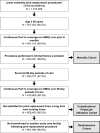
Methods: Observed rates of mortality, complications, and readmissions were calculated over 90-day episodes of care among Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries who received elective knee arthroplasty and elective or nonelective hip arthroplasty procedures in 2013-2014 (N = 640,021). Post-acute care utilization of skilled nursing and inpatient rehabilitation facilities was collected from Medicare files.
Results: Mortality rates over 90 days were 0.4% (knee arthroplasty), 0.5% (elective hip arthroplasty), and 13.4% (nonelective hip arthroplasty). Complication rates were 2.1% (knee arthroplasty), 3.0% (elective hip arthroplasty), and 8.5% (nonelective hip arthroplasty). Inpatient rehabilitation facility utilization rates were 6.0% (knee arthroplasty), 6.7% (elective hip arthroplasty), and 23.5% (nonelective hip arthroplasty). Skilled nursing facility utilization rates were 33.9% (knee arthroplasty), 33.4% (elective hip arthroplasty), and 72.1% (nonelective hip arthroplasty). Readmission rates were 6.3% (knee arthroplasty), 7.0% (elective hip arthroplasty), and 19.2% (nonelective hip arthroplasty). Patients' age and clinical characteristics yielded consistent patterns across all outcomes.
Conclusion: Outcomes in our national cohort of Medicare beneficiaries receiving lower extremity joint arthroplasties varied across procedure types and patient characteristics. Future research examining trends in access to care, resource use, and care quality over bundled episodes will be important for addressing the challenges of value-based payment reform.
Keywords: bundled payments; complications; mortality; post–acute care; readmissions.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Burwell SM. Setting value-based payment goals–HHS efforts to improve U.S. health care. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:897–9. - PubMed
-
- Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Federal Register. Medicare Program; Comprehensive Care for Joint Replacement Payment Model for Acute Care Hospitals Furnishing Lower Extremity Joint Replacement Services; Final Rule. 2015 - PubMed
-
- Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Report to the Congress: Medicare Payment Policy. 2016 Mar; Available at: http://medpac.gov/documents/reports/march-2016-report-to-the-congress-me.... Accessed 7/20/2016.
-
- Yale New Haven Health Services Corporation/Center for Outcomes Research & Evaluation. 2016 Procedure-Specific Measure Updates and Specifications Report, Hospital-Level Risk-Standardized Complication Measure Elective Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) and/or Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)-Version 5.0. Available at: https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-Initiatives-Patient-Assessment-Inst.... Accessed 7/15/2016.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

