Filaments and fingers: Novel structural aspects of the single septin from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- PMID: 28476887
- PMCID: PMC5491775
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.762229
Filaments and fingers: Novel structural aspects of the single septin from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Abstract
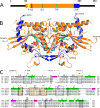
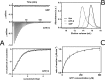
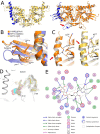
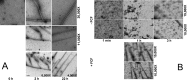
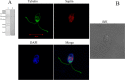
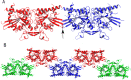
Septins are filament-forming GTP-binding proteins involved in many essential cellular events related to cytoskeletal dynamics and maintenance. Septins can self-assemble into heterocomplexes, which polymerize into highly organized, cell membrane-interacting filaments. The number of septin genes varies among organisms, and although their structure and function have been thoroughly studied in opisthokonts (including animals and fungi), no structural studies have been reported for other organisms. This makes the single septin from Chlamydomonas (CrSEPT) a particularly attractive model for investigating whether functional homopolymeric septin filaments also exist. CrSEPT was detected at the base of the flagella in Chlamydomonas, suggesting that CrSEPT is involved in the formation of a membrane-diffusion barrier. Using transmission electron microscopy, we observed that recombinant CrSEPT forms long filaments with dimensions comparable with those of the canonical structure described for opisthokonts. The GTP-binding domain of CrSEPT purified as a nucleotide-free monomer that hydrolyzes GTP and readily binds its analog guanosine 5'-3-O-(thio)triphosphate. We also found that upon nucleotide binding, CrSEPT formed dimers that were stabilized by an interface involving the ligand (G-interface). Across this interface, one monomer supplied a catalytic arginine to the opposing subunit, greatly accelerating the rate of GTP hydrolysis. This is the first report of an arginine finger observed in a septin and suggests that CrSEPT may act as its own GTP-activating protein. The finger is conserved in all algal septin sequences, suggesting a possible correlation between the ability to form homopolymeric filaments and the accelerated rate of hydrolysis that it provides.
Keywords: Chlamydomonas; GTPase; algae; arginine finger; crystal structure; filament; septin.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

References
-
- Hartwell L. H. (1971) Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. IV. Genes controlling bud emergence and cytokinesis. Exp. Cell Res. 69, 265–276 - PubMed
-
- Longtine M. S., DeMarini D. J., Valencik M. L., Al-Awar O. S., Fares H., De Virgilio C., and Pringle J. R. (1996) The septins: roles in cytokinesis and other processes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 8, 106–119 - PubMed
-
- Kinoshita M. (2006) Diversity of septin scaffolds. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 18, 54–60 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

