Implementation of the Edmonton Symptom Assessment System for Symptom Distress Screening at a Community Cancer Center: A Pilot Program
- PMID: 28476945
- PMCID: PMC5553963
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0500
Implementation of the Edmonton Symptom Assessment System for Symptom Distress Screening at a Community Cancer Center: A Pilot Program
Abstract
Background: Distress screening is mandated by the American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer; however, there is limited literature on its impact in actual practice. We examined the impact of a pilot distress screening program on access to psychosocial care.
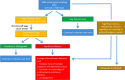
Methods: Edmonton Symptom Assessment System (ESAS) screening was routinely conducted at our community-based medical oncology program. Patients who screened positive for severe distress were sent to a social worker for triage and referred to the appropriate services if indicated. We compared the proportion of patients who had ESAS completed, the proportion of patients who screened positive, and the number of patients who had social work assessment and palliative care consultation over the preimplementation (September 2015), training (October/November 2015), and postimplementation (December 2015) periods.
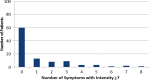
Results: A total of 379, 328, and 465 cancer patients were included in the preimplementation, training, and postimplementation periods, respectively. The proportion of patients who completed ESAS increased over time (83% vs. 91% vs. 96%). Among the patients who had completed ESAS, between 11% and 13% were positive for severe distress, which remained stable over the three periods. We observed a significant increase in social work referrals for psychosocial assessment (21% vs. 71% vs. 79%). There was also a trend towards an increased number of palliative care referrals (12% vs. 20% vs. 28%).
Conclusion: Our community-based cancer center implemented distress screening rapidly in a resource-limited setting, with a notable increase in symptom documentation and psychosocial referral.
Implications for practice: The American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer mandates distress screening; however, there is limited literature on how this process should be implemented and its impact on clinical practice. We used the Edmonton Symptom Assessment System for routine symptom distress screening in a community-based medical oncology program that provides care for an underserved population. Comparing before and after program implementation, we found an increase in the number of documentations of symptom burden and an increase in psychosocial referrals. Findings from this study may inform the implementation of routine symptom distress screening in cancer patients.
Keywords: Health plan implementation; Mass screening; Neoplasms; Palliative care; Psychological stress; Symptom assessment.
© AlphaMed Press 2017.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of potential conflicts of interest may be found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Hui D, Bruera E. Supportive and palliative oncology: A new paradigm for comprehensive cancer care. Hematol Oncol Rev 2013;9:68–74.
-
- Portenoy RK, Thaler HT, Kornblith AB et al. Symptom prevalence, characteristics and distress in a cancer population. Qual Life Res 1994;3:183–189. - PubMed
-
- Zeng L, Zhang L, Culleton S et al. Edmonton symptom assessment scale as a prognosticative indicator in patients with advanced cancer. J Palliat Med 2011;14:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Mercadante S, Valle A, Porzio G et al. Prognostic factors of survival in patients with advanced cancer admitted to home care. J Pain Symptom Manage 2013; 45:56–62. - PubMed
-
- Pearman T, Garcia S, Penedo F et al. Implementation of distress screening in an oncology setting. J Community Support Oncol 2015;13:423–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

