Substitutional Analysis of Orthologous Protein Families Using BLOCKS
- PMID: 28479743
- PMCID: PMC5405086
- DOI: 10.6026/97320630013001
Substitutional Analysis of Orthologous Protein Families Using BLOCKS
Abstract
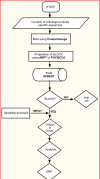
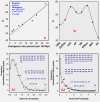
Orthologous proteins, form due to divergence of parental sequence, perform similar function under different environmental and biological conditions. Amino acid changes at locus specific positions form hetero-pairs whose role in BLOCK evolution is yet to be understood. We involve eight protein BLOCKs of known divergence rate to gain insight into the role of hetero-pairs in evolution. Our procedure APBEST uses BLOCK-FASTA file to extract BLOCK specific evolutionary parameters such as dominantly used hetero-pair (D), usage of hetero-pairs (E), non-conservative to conservative substitution ratio (R), maximally-diverse residue (MDR), residue (RD) and class (CD) specific diversity. All these parameters show BLOCK specific variation. Conservative nature of D points towards restoration of function of BLOCK. While E sets the upper-limit of usage of hereto-pairs, strong correlation of R with divergence-rate indicates that the later is directly dependent on non-conservative substitutions. The observation that MDR, measure of positional diversity, occupy very limited positions in BLOCK indicates accommodation of diversity is positionally restricted. Overall, the study extract observed hetero-pair related quantitative and multi-parametric details of BLOCK, which finds application in evolutionary biology.
Keywords: conservative; divergence rate; evolution; hetero-pairs; non-conservative; substitution.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Heterotachy and functional shift in protein evolution.IUBMB Life. 2003 Apr-May;55(4-5):257-65. doi: 10.1080/1521654031000123330. IUBMB Life. 2003. PMID: 12880207 Review.
-
Algorithms for computing parsimonious evolutionary scenarios for genome evolution, the last universal common ancestor and dominance of horizontal gene transfer in the evolution of prokaryotes.BMC Evol Biol. 2003 Jan 6;3:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-3-2. Epub 2003 Jan 6. BMC Evol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12515582 Free PMC article.
-
The nonsynonymous/synonymous substitution rate ratio versus the radical/conservative replacement rate ratio in the evolution of mammalian genes.Mol Biol Evol. 2007 Oct;24(10):2235-41. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm152. Epub 2007 Jul 25. Mol Biol Evol. 2007. PMID: 17652332
-
Nucleotide sequence divergence and functional constraint in mRNA evolution.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7328-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7328. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980. PMID: 6938980 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of protein stability and function.Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:289-310. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001445. Annu Rev Genet. 1989. PMID: 2694933 Review.
Cited by
-
PROPAB: Computation of Propensities and Other Properties from Segments of 3D structure of Proteins.Bioinformation. 2018 May 31;14(5):190-193. doi: 10.6026/97320630014190. eCollection 2018. Bioinformation. 2018. PMID: 30108414 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of protein microenvironment in tannase industrial applicability: An in-silico comparative study of pathogenic and non-pathogenic bacterial tannase.Heliyon. 2020 Nov 11;6(11):e05359. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05359. eCollection 2020 Nov. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33241136 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of salt-bridges in prolyl oligopeptidase from Pyrococcus furiosus and Homo sapiens.Bioinformation. 2019 Mar 15;15(3):214-225. doi: 10.6026/97320630015214. eCollection 2019. Bioinformation. 2019. PMID: 31354198 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights from water-ferredoxin interaction in mesophilic algae and halophilic archaea.Bioinformation. 2019 Feb 28;15(2):79-89. doi: 10.6026/97320630015079. eCollection 2019. Bioinformation. 2019. PMID: 31435153 Free PMC article.
-
POWAINDv1.0: A Program for Protein-Water Interactions Determination.Bioinformation. 2018 Dec 22;14(9):530-539. doi: 10.6026/97320630014530. eCollection 2018. Bioinformation. 2018. PMID: 31223212 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
