Penile necrosis secondary to purpura fulminans: a case report and review of literature
- PMID: 28479975
- PMCID: PMC5411736
- DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjx078
Penile necrosis secondary to purpura fulminans: a case report and review of literature
Abstract
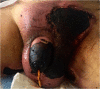
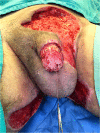
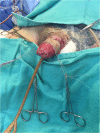
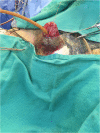
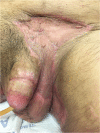
We report the case of a 60-year-old Hispanic male with widespread necrotic purpuric lesions involving the penile, suprapubic, inguinal and hip dermis due to purpura fulminans. Purpura fulminans describes a rare syndrome involving intravascular thrombosis and hemorrhagic infarction of the skin; this rapidly progressing syndrome features vascular collapse and disseminated intravascular coagulation. This patient's penile necrosis involved the majority of the penile shaft and glans penis, and ultimately required partial glansectomy and repeated debridement for treatment. Subsequently, full thickness skin grafting was completed for reconstruction with good effect. While reports of penile necrosis secondary to various causes are documented in the literature, no prior reports describe penile necrosis secondary to purpura fulminans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Penile Necrosis as a Presenting Sign of Purpura Fulminans Mimicking Fournier's Gangrene.Am J Dermatopathol. 2021 Jan 1;43(1):e13-e15. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000001744. Am J Dermatopathol. 2021. PMID: 32675467
-
Acute purpura fulminans-a rare cause of skin necrosis: A single-institution clinicopathological experience.J Cutan Pathol. 2020 Nov;47(11):1003-1009. doi: 10.1111/cup.13732. Epub 2020 Sep 13. J Cutan Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32356378
-
Uncommon Location of Purpura Fulminans: Case Report and Literature Review.Case Rep Dermatol. 2020 Jan 15;12(1):5-11. doi: 10.1159/000505476. eCollection 2020 Jan-Apr. Case Rep Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32095125 Free PMC article.
-
Massive soft tissue infections: necrotizing fasciitis and purpura fulminans.J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2005;15(1):57-65. doi: 10.1615/jlongtermeffmedimplants.v15.i1.70. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2005. PMID: 15715517 Review.
-
Spectrum of purpura fulminans: report of three classical prototypes and review of management strategies.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012 Mar-Apr;78(2):228. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.93655. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012. PMID: 22421668 Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report: Glans penile necrosis in a patient with SARS-CoV-2 and leprosy infection.F1000Res. 2024 Feb 5;11:142. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.84355.4. eCollection 2022. F1000Res. 2024. PMID: 39233873 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical outcomes in adults with purpura fulminans: a systematic review and patient-level meta-synthesis.Burns Trauma. 2019 Oct 18;7:30. doi: 10.1186/s41038-019-0168-x. eCollection 2019. Burns Trauma. 2019. PMID: 31641673 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mazzone L, Schiestl C. Management of septic skin necroses. Eur J Pediatr Surg 2013;23:349–58. - PubMed
-
- Lowery K, Shirley R, Shelley OP, Kaniorou-Larai M, Philp B, Dziewulski P. Purpura fulminans skin loss: surgical management protocols at a regional burns centre. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2008;61:1520–3. - PubMed
-
- Morris ME, Maijub JG, Walker SK, Gardner GP, Jones RG. Meningococcal sepsis and purpura fulminans: the surgical perspective. Postgrad Med J 2013;89:340–5. - PubMed
-
- Roughton MC, Agarwal S, Gottlieb LJ. Surgical management of acute infectious purpura fulminans. J Burn Care Res 2011;32:231–6. - PubMed
-
- Chalmers E, Cooper P, Forman K, Grimley C, Khair K, Minford A, et al. . Purpura fulminans: recognition, diagnosis and management. Arch Dis Child 2011;96:1066–71. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources