Selective internal radiation therapy with SIR-Spheres in hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 28480066
- PMCID: PMC5401864
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo.2016.11.08
Selective internal radiation therapy with SIR-Spheres in hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
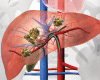
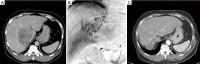
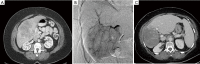
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) often present at stages where patients have limited treatment options. Use of selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) with yttrium-90 (Y-90) resin microspheres has progressed as data increasingly speak to its utility in patients with both intermediate and late stage disease in these cancers. In anticipation of the pending completion of several prospective randomized controlled multicenter studies exploring the use of Y-90 resin microspheres in primary liver cancers, this article outlines mechanisms involved in SIRT administration and reviews key efficacy and safety data that are currently available in the literature involving use of this therapy in both HCC and ICC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); SIR-Spheres; intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC); radioembolization; yttrium-90 resin microspheres.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: EA Wang is a training proctor for Sirtex Medical. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Kennedy A, Nag S, Salem R, et al. Recommendations for radioembolization of hepatic malignancies using yttrium-90 microsphere brachytherapy: a consensus panel report from the radioembolization brachytherapy oncology consortium. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007;68:13-23. 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.11.060 - DOI - PubMed
-
- SIRTEX. SIR-Spheres microspheres (Yttrium-90 Microspheres) package insert. 2014.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
