Systemic sclerosis associated with colliquative necrosis in the cerebellum
- PMID: 28480106
- PMCID: PMC5402329
- DOI: 10.4103/sni.sni_401_16
Systemic sclerosis associated with colliquative necrosis in the cerebellum
Abstract
Background: The scleroderma is a complex autoimmune collagen disorder that can affect many organs simultaneously, as it occurs in the systemic sclerosis (SS), or only the skin, as it occurs in the localized scleroderma (LS). The neurological presentation is extremely uncommon, and even more uncommon are the symptoms of the scleroderma in the cerebellum.
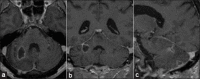
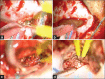
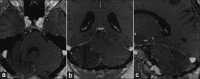
Case description: We report the case of a 56-year-old male with cerebellar lesions mimicking a brain abscess. After surgical excision, the histopathological diagnosis deposed for an ischemic necrosis caused by a vasculopathy. All the bacteriological and viral exams were negative, whereas the rheumatologic tests were compatible with the scleroderma pattern.
Conclusion: Up to now, the literature has described only 5 cases of scleroderma in the posterior cranial fossa. The authors report a case of SS causing colliquative necrosis in the cerebellum. Pathogenetic mechanisms, clinical aspects, and radiological features are discussed along with the pertinent literature.
Keywords: Cerebellum; colliquative necrosis; posterior cranial fossa; scleroderma.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chiang CH, Liu CJ, Huang CC, Chan WL, Huang PH, Chen TJ, et al. Systemic sclerosis and risk of ischaemic stroke: A nationwide cohort study. Rheumatology. 2013;52:161–5. - PubMed
-
- Das CP, Prabhakar S, Lal V, Kharbanda PS. Scleroderma, stroke, optic neuropathy: A rare association. Neurol India. 2002;50:504–7. - PubMed
-
- Estey E, Lieberman A, Pinto R, Meltzer M, Ransohoff J. Cerebral arteritis in scleroderma. Stroke. 1979;10:595–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
