COGNITIVE-ENHANCING PROPERTIES OF MORINDA LUCIDA (RUBIACEAE) AND PELTOPHORUM PTEROCARPUM (FABACEAE) IN SCOPOLAMINE-INDUCED AMNESIC MICE
- PMID: 28480424
- PMCID: PMC5412218
- DOI: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i3.14
COGNITIVE-ENHANCING PROPERTIES OF MORINDA LUCIDA (RUBIACEAE) AND PELTOPHORUM PTEROCARPUM (FABACEAE) IN SCOPOLAMINE-INDUCED AMNESIC MICE
Abstract
Background: Cognitive disorders associated with aging have been successfully managed by African traditional medical practitioners using various plants. This study evaluated the cognitive enhancing potentials of Morinda lucida (L) Rubiaceae and Peltophorum pterocarpum (DC) ex. K Heyne in scopolamine induced amnesic animals.
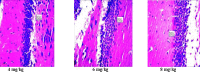
Materials and methods: The anti-amnesic activity of the ethyl acetate extracts of Morinda lucida and Peltophorum pterocarpum at doses of 4 mg/kg, 6 mg/kg and 8 mg/kg were assessed in scopolamine induced amnesic mice using Morris water maze test model. Effect of the extracts on the histology of the hippocampus was also evaluated.
Results: The ethyl acetate extract of Morinda lucida and Peltophorum pterocarpum ameliorated scopolamine induced memory deficit in the animals under study. There was no effect of the extract on the histology of the hippocampus. However, there was an increase in the density of cells in the hippocampus of treated group as compared to the untreated.
Conclusion: Morinda lucida and Peltophorum pterocarpum showed considerable enhancement of cognition in scopolamine induced amnesic mice.
Keywords: Hippocampus; Morinda lucida; Morris water maze; Peltophorum pterocarpum; Scopolamine.
Figures
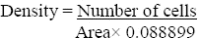



Similar articles
-
The ethanolic extract of the Eclipta prostrata L. ameliorates the cognitive impairment in mice induced by scopolamine.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 22;190:165-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.010. Epub 2016 Jun 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27267831
-
Evaluation of anti-amnesic effect of extracts of selected Ocimum species using in-vitro and in-vivo models.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Dec 4;193:490-499. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.10.026. Epub 2016 Oct 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27725240
-
Cognitive enhancing effects of alpha asarone in amnesic mice by influencing cholinergic and antioxidant defense mechanisms.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2012;76(8):1518-22. doi: 10.1271/bbb.120247. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22878197
-
Beneficial effects of Brassica juncea on cognitive functions in rats.Pharm Biol. 2013 Oct;51(10):1304-10. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2013.789917. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Pharm Biol. 2013. PMID: 23848339
-
Ameliorative effect of betulin from Betula platyphylla bark on scopolamine-induced amnesic mice.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2016;80(1):166-71. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2015.1072460. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26287580
Cited by
-
Antioxidant and Cell Proliferation Properties of the Vietnamese Traditional Medicinal Plant Peltophorum pterocarpum.Molecules. 2020 Oct 19;25(20):4800. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204800. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33086647 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Herb-Drug Interactions in the Management of Age-Related Cognitive Dysfunction.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jan 19;13(1):124. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13010124. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33478035 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Auld D. S, Kornecook T. J, Bastianetto S, Quirion R. Alzheimer’s disease and the basal forebrain cholinergic system: relation to βamyloid peptides, cognition and treatment strategies. Progress in neurobiology. 2002;68(3):209–245. - PubMed
-
- Bejar C, Wang R. H, Weinstock M. Effect of rivastigmine on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats. Europrean Journal of Pharmacology. 1999;383:231–240. - PubMed
-
- Broks P, Preston G. C, Traub M, Poppleton P, Ward C, Stahl S. M. Modelling dementia: effects of scopolamine on memory and attention. Neuropsychologia. 1988;26(5):685–700. - PubMed
-
- Buckner R. L. Memory and executive function in aging and AD: Multiple factors that cause decline and reverse factors than compensate. Neuron. 2004;44(1):195–208. - PubMed
-
- Elufioye T. O, Obuotor E. F, Agbedahunsi J. M, Adesanya S. A. Cholinesterase inhibitory activity of Morinda lucida benth. Journal of Pharmacognosy and phytotherapy. 2013;5:77–82.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
