THE HERBAL MIXTURE XIAO-CHAI-HU TANG (XCHT) INDUCES APOPTOSIS OF HUMAN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA HUH7 CELLS IN VITRO AND IN VIVO
- PMID: 28480435
- PMCID: PMC5412230
- DOI: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i3.25
THE HERBAL MIXTURE XIAO-CHAI-HU TANG (XCHT) INDUCES APOPTOSIS OF HUMAN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA HUH7 CELLS IN VITRO AND IN VIVO
Abstract
Background: Xiao-Chai-Hu Tang (XCHT) is an extract of seven herbs with anticancer properties, but its mechanism of action is unknown. In this study, we evaluated XCHT-treated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) for anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects.
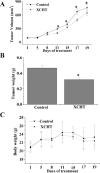
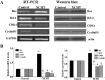
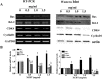
Materials and methods: Using a hepatic cancer xenograft model, we investigated the in vivo efficacy of XCHT against tumor growth by evaluating tumor volume and weight, as well as measuring apoptosis and cellular proliferation within the tumor. To study the effects of XCHT in vitro, we measured the cell viability of XCHT-treated Huh7 cells, as well as colony formation and apoptosis. To identify a potential mechanism of action, the gene and protein expression levels of Bax, Bcl-2, CDK4 and cyclin-D1 were measured in XCHT-treated Huh7 cells.
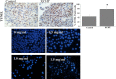
Results: We found that XCHT reduced tumor size and weight, as well as significantly decreased cell viability both in vivo and in vitro. XCHT suppressed the expression of the proliferation marker Ki-67 in HCC tissues and inhibited Huh7 colony formation. XCHT induced apoptosis in HCC tumor tissues and in Huh7 cells. Finally, XCHT altered the expression of Bax, Bcl-2, CDK4 and cyclin-D1, which halted cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that XCHT enhances expression of pro-apoptotic pathways, resulting in potent anticancer activity.
Keywords: Xiao-Chai-Hu Tang; apoptosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; proliferation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang ameliorates tumor growth in cancer comorbid depressive symptoms via modulating gut microbiota-mediated TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2021 Jul 15;88:153606. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153606. Epub 2021 May 24. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34111616 Clinical Trial.
-
Xiao-Chai-Hu Tang in treating model mice with D-galactosamine-induced liver injury.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012 Apr 2;9(3):405-11. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v9i3.16. eCollection 2012. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012. PMID: 23983374 Free PMC article.
-
Swainsonine inhibits growth and potentiates the cytotoxic effect of paclitaxel in hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo.Oncol Rep. 2012 Dec;28(6):2091-100. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.2035. Epub 2012 Sep 17. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22993037
-
Xiao Chai Hu Tang for Peptic Ulcers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Apr 29;2021:6693677. doi: 10.1155/2021/6693677. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34012475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision Strike Strategy for Liver Diseases Trilogy with Xiao-Chai-Hu Decoction: A Meta-Analysis with Machine Learning.Phytomedicine. 2025 Jul;142:156796. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156796. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40347886
Cited by
-
Multitargeted Herbal Prescription So Shiho Tang: A Scoping Review on Biomarkers for the Evaluation of Therapeutic Effects.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Sep 27;16(10):1371. doi: 10.3390/ph16101371. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895842 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking study on the mechanism of colorectal cancer treatment using Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 14;16(6):e0252508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252508. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34125845 Free PMC article.
-
Korean traditional herbal formula Soshiho-tang attenuates memory impairment and neuronal damage in mice with amyloid-beta-induced Alzheimer's disease.Integr Med Res. 2021 Sep;10(3):100723. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2021.100723. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Integr Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33898246 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of the Mechanisms and Molecular Targets of Shuanglian Decoction for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Network Pharmacology.ACS Omega. 2020 Dec 31;6(1):917-924. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05550. eCollection 2021 Jan 12. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33458543 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic exploration and experimental validation of the Xiaochaihu decoction for the treatment of breast cancer by network pharmacology.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 May 13;16(9):7979-7999. doi: 10.18632/aging.205798. Epub 2024 May 13. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38742934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y, Robles AI, Martinez LA, Liu F, Gimenez-Conti IB, Conti CJ. Expression of G1 cyclins, cyclin -dependent kinases, and cyclin- dependent kinase inhibitors in androgen- induced prostate proliferation in castrated rats. Cell Growth Differ. 1996;7(11):1571–1578. - PubMed
-
- Cory S, Adams JM. The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(9):647–656. - PubMed
-
- Cui X, Wang Y, Kokudo N, Fang D, Tang W. Traditional Chinese medicine and related active compounds against hepatitis B virus infection. Biosci Trends. 2010;4(2):39–47. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
