Integrated continuous bioprocessing: Economic, operational, and environmental feasibility for clinical and commercial antibody manufacture
- PMID: 28480535
- PMCID: PMC5575510
- DOI: 10.1002/btpr.2492
Integrated continuous bioprocessing: Economic, operational, and environmental feasibility for clinical and commercial antibody manufacture
Abstract
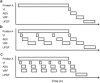
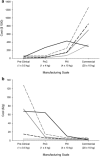
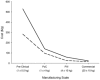
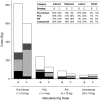
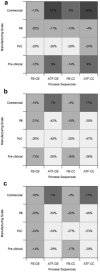
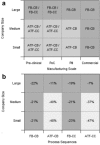
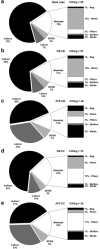
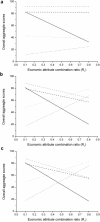
This paper presents a systems approach to evaluating the potential of integrated continuous bioprocessing for monoclonal antibody (mAb) manufacture across a product's lifecycle from preclinical to commercial manufacture. The economic, operational, and environmental feasibility of alternative continuous manufacturing strategies were evaluated holistically using a prototype UCL decisional tool that integrated process economics, discrete-event simulation, environmental impact analysis, operational risk analysis, and multiattribute decision-making. The case study focused on comparing whole bioprocesses that used either batch, continuous or a hybrid combination of batch and continuous technologies for cell culture, capture chromatography, and polishing chromatography steps. The cost of goods per gram (COG/g), E-factor, and operational risk scores of each strategy were established across a matrix of scenarios with differing combinations of clinical development phase and company portfolio size. The tool outputs predict that the optimal strategy for early phase production and small/medium-sized companies is the integrated continuous strategy (alternating tangential flow filtration (ATF) perfusion, continuous capture, continuous polishing). However, the top ranking strategy changes for commercial production and companies with large portfolios to the hybrid strategy with fed-batch culture, continuous capture and batch polishing from a COG/g perspective. The multiattribute decision-making analysis highlighted that if the operational feasibility was considered more important than the economic benefits, the hybrid strategy would be preferred for all company scales. Further considerations outside the scope of this work include the process development costs required to adopt continuous processing. © 2017 The Authors Biotechnology Progress published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Institute of Chemical Engineers Biotechnol. Prog., 33:854-866, 2017.
Keywords: antibody manufacture; continuous chromatography; fed-batch; perfusion culture; process economics.
© 2017 The Authors Biotechnology Progress published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Figures
References
-
- DiMasi JA, Feldman L, Seckler A, Wilson A. Trends in risks associated with new drug development: success rates for investigational drugs. Clin Pharmacol Therap. 2010;87:272–277. - PubMed
-
- Farid SS. Process economics drivers in industrial monoclonal antibody manufacture In: Gottschalk U, editor. Process Scale Purification of Antibodies: Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2009;239–262.
-
- Morgan S, Grootendorst P, Lexchin J, Cunningham C, Greyson D. The cost of drug development: a systematic review. Health Policy. 2011;100:4–17. - PubMed
-
- Paul SM, Mytelka DS, Dunwiddie CT, Persinger CC, Munos BH, Lindborg SR, Schacht AL. How to improve R&D productivity: the pharmaceutical industry's grand challenge. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:203–214. - PubMed
-
- Bogdan B, Villiger R. 2010. Valuation in Life Sciences. Valuation in Life Sciences: A Practical Guide, Third Edition:67–303.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

