Prognostic value of nighttime blood pressure load in Chinese patients with nondialysis chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 28480628
- PMCID: PMC8031363
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.13017
Prognostic value of nighttime blood pressure load in Chinese patients with nondialysis chronic kidney disease
Abstract
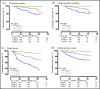
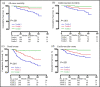
The prognostic value of nighttime blood pressure (BP) load in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) remains unknown. The prognostic value of nighttime BP load in a cohort of Chinese patients with nondialysis CKD was investigated. The authors monitored ambulatory BP and followed health outcomes in 588 Chinese CKD patients. Multivariable-adjusted Cox regression analyses indicated that nighttime BP load was a significant risk factor for all clinical outcomes in CKD patients, even when adjusted for clinic BP. Tertile 3 of systolic BP load (vs tertile 1) was associated with an increased risk of renal events (hazard ratio [HR], 2.21; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.12-4.38) and cardiovascular events (HR, 5.34; 95% CI, 1.58-18.04); tertile 3 of diastolic BP load (vs tertile 1) was associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality (HR, 6.73; 95% CI, 1.79-25.20), cardiovascular mortality (HR, 7.18; 95% CI, 1.47-35.03), renal events (HR, 2.40; 95% CI, 1.17-4.92), and cardiovascular events (HR, 5.87; 95% CI, 1.97-17.52). Higher nighttime BP load, especially nighttime diastolic BP load, was associated with a poorer prognosis in Chinese nondialysis CKD patients.
Keywords: cardiovascular events; chronic kidney disease; mortality; nighttime blood pressure load; prognosis.
©2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Agarwal R, Andersen MJ. Blood pressure recordings within and outside the clinic and cardiovascular events in chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol. 2006;26:503‐510. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal R, Andersen MJ. Prognostic importance of ambulatory blood pressure recordings in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2006;69:1175‐1180. - PubMed
-
- Minutolo R, Agarwal R, Borrelli S, et al. Prognostic role of ambulatory blood pressure measurement in patients with nondialysis chronic kidney disease. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171:1090‐1098. - PubMed
-
- Zachariah PK, Sheps SG, Bailey KR, Wiltgen CM, Moore AG. Age‐related characteristics of ambulatory blood pressure load and mean blood pressure in normotensive subjects. JAMA. 1991;265:1414‐1417. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

