Impact of Neurointensivist Co-management on the Clinical Outcomes of Patients Admitted to a Neurosurgical Intensive Care Unit
- PMID: 28480662
- PMCID: PMC5426243
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.6.1024
Impact of Neurointensivist Co-management on the Clinical Outcomes of Patients Admitted to a Neurosurgical Intensive Care Unit
Abstract
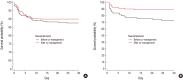
Limited data are available on improved outcomes after initiation of neurointensivist co-management in neurosurgical intensive care units (NSICUs) in Korea. We evaluated the impact of a newly appointed neurointensivist on the outcomes of neurosurgical patients admitted to an intensive care unit (ICU). This retrospective observational study involved neurosurgical patients admitted to the NSICU at Samsung Medical Center between March 2013 and May 2016. Neurointensivist co-management was initiated in October 1 2014. We compared the outcomes of neurosurgical patients before and after neurointensivist co-management. The primary outcome was ICU mortality. A total of 571 patients were admitted to the NSICU during the study period, 291 prior to the initiation of neurointensivist co-management and 280 thereafter. Intracranial hemorrhage (29.6%) and traumatic brain injury (TBI) (26.6%) were the most frequent reasons for ICU admission. TBI was the most common cause of death (39.0%). There were no significant differences in mortality rates and length of ICU stay before and after co-management. However, the rates of ICU and 30-day mortality among the TBI patients were significantly lower after compared to before initiation of neurointensivist co-management (8.5% vs. 22.9%; P = 0.014 and 11.0% vs. 27.1%; P = 0.010, respectively). Although overall outcomes were not different after neurointensivist co-management, initiation of a strategy of routine involvement of a neurointensivist significantly reduced the ICU and 30-day mortality rates of TBI patients.
Keywords: Critical Care Outcomes; Intensive Care Unit; Neurosurgery.
© 2017 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Josephson SA, Douglas VC, Lawton MT, English JD, Smith WS, Ko NU. Improvement in intensive care unit outcomes in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage after initiation of neurointensivist co-management. J Neurosurg. 2010;112:626–630. - PubMed
-
- Varelas PN, Eastwood D, Yun HJ, Spanaki MV, Hacein Bey L, Kessaris C, Gennarelli TA. Impact of a neurointensivist on outcomes in patients with head trauma treated in a neurosciences intensive care unit. J Neurosurg. 2006;104:713–719. - PubMed
-
- Suarez JI, Zaidat OO, Suri MF, Feen ES, Lynch G, Hickman J, Georgiadis A, Selman WR. Length of stay and mortality in neurocritically ill patients: impact of a specialized neurocritical care team. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:2311–2317. - PubMed
-
- Morrow DA, Fang JC, Fintel DJ, Granger CB, Katz JN, Kushner FG, Kuvin JT, Lopez-Sendon J, McAreavey D, Nallamothu B, et al. Evolution of critical care cardiology: transformation of the cardiovascular intensive care unit and the emerging need for new medical staffing and training models: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2012;126:1408–1428. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

