Emerging Roles of microRNAs in Ischemic Stroke: As Possible Therapeutic Agents
- PMID: 28480877
- PMCID: PMC5466283
- DOI: 10.5853/jos.2016.01368
Emerging Roles of microRNAs in Ischemic Stroke: As Possible Therapeutic Agents
Abstract
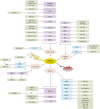
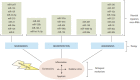
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and physical disability worldwide. The consequences of stroke injuries are profound and persistent, causing in considerable burden to both the individual patient and society. Current treatments for ischemic stroke injuries have proved inadequate, partly owing to an incomplete understanding of the cellular and molecular changes that occur following ischemic stroke. MicroRNAs (miRNA) are endogenously expressed RNA molecules that function to inhibit mRNA translation and have key roles in the pathophysiological processes contributing to ischemic stroke injuries. Potential therapeutic areas to compensate these pathogenic processes include promoting angiogenesis, neurogenesis and neuroprotection. Several miRNAs, and their target genes, are recognized to be involved in these recoveries and repair mechanisms. The capacity of miRNAs to simultaneously regulate several target genes underlies their unique importance in ischemic stroke therapeutics. In this Review, we focus on the role of miRNAs as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, as well as promising therapeutic agents in cerebral ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Ischemia; MicroRNAs; Stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Heron M. Deaths: leading causes for 2004. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2007;56:1–96. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Prevalence of disabilities and associated health conditions among adults--United Sstates, 1999. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001;50:120–125. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . The World health report 2004: changing history. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2004.
-
- Mukherjee D, Patil CG. Epidemiology and the global burden of stroke. World Neurosurg. 2011;76(6 Suppl):S85–S90. - PubMed
-
- Beal CC. Gender and stroke symptoms: a review of the current literature. J Neurosci Nurs. 2010;42:80–87. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

