Antigen-inexperienced memory CD8+ T cells: where they come from and why we need them
- PMID: 28480897
- PMCID: PMC5569888
- DOI: 10.1038/nri.2017.34
Antigen-inexperienced memory CD8+ T cells: where they come from and why we need them
Abstract
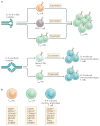
Memory-phenotype CD8+ T cells exist in substantial numbers within hosts that have not been exposed to either foreign antigen or overt lymphopenia. These antigen-inexperienced memory-phenotype T cells can be divided into two major subsets: 'innate memory' T cells and 'virtual memory' T cells. Although these two subsets are nearly indistinguishable by surface markers alone, notable developmental and functional differences exist between the two subsets, which suggests that they represent distinct populations. In this Opinion article, we review the available literature on each subset, highlighting the key differences between these populations. Furthermore, we suggest a unifying model for the categorization of antigen-inexperienced memory-phenotype CD8+ T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
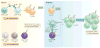
Comment in
-
Foreign antigen-independent memory-phenotype CD4+ T cells: a new player in innate immunity?Nat Rev Immunol. 2018 Feb 26;18(3):1. doi: 10.1038/nri.2018.12. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29480287 No abstract available.
-
Foreign antigen-independent memory-phenotype CD4+ T cells: a new player in innate immunity?Nat Rev Immunol. 2018 Feb 26;18(3):1. doi: 10.1038/nri.2018.13. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29480288 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

