Loss of H2B monoubiquitination is associated with poor-differentiation and enhanced malignancy of lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 28481029
- PMCID: PMC5527746
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.30769
Loss of H2B monoubiquitination is associated with poor-differentiation and enhanced malignancy of lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
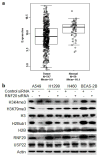
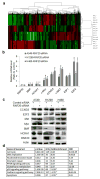
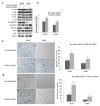
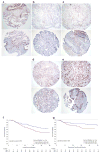
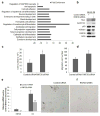
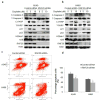
Deregulated monoubiquitination of histone H2B (H2Bub1), mainly catalyzed by E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF20/RNF40 complex, may play an important role in cancer. Here we investigate potential roles of H2Bub1 and the underlying mechanisms through which it contributes to cancer development and progression in lung adenocarcinoma. We show that downregulation of H2Bub1 through RNF20 knockdown dramatically decreases H3K79 and H3K4 trimethylation in both normal and malignant lung epithelial cell lines. Concurrently, global transcriptional profiling analysis reveals that multiple tumor-associated genes such as CCND3, E2F1/2, HOXA1, Bcl2 modifying factor (BMF), Met, and Myc; and signaling pathways of cellular dedifferentiation, proliferation, adhesion, survival including p53, cadherin, Myc, and anti-apoptotic pathways are differentially expressed or significantly altered in these lung epithelial cells upon downregulation of H2Bub1. Moreover, RNF20 knockdown dramatically suppresses terminal squamous differentiation of cultured bronchial epithelial cells, and significantly enhances proliferation, migration, invasion, and cisplatin resistance of lung cancer cells. Furthermore, immunohistochemistry analysis shows that H2Bub1 is extremely low or undetectable in >70% of 170 lung adenocarcinoma samples. Notably, statistical analysis demonstrates that loss of H2Bub1 is significantly correlated with poor differentiation in lung adenocarcinoma (p = 0.0134). In addition, patients with H2Bub1-negative cancers had a trend towards shorter survival compared with patients with H2Bub1-positive cancers. Taken together, our findings suggest that loss of H2Bub1 may enhance malignancy and promote disease progression in lung adenocarcinoma probably through modulating multiple cancer signaling pathways.
Keywords: H2B monoubiquitination; RNF20; differentiation; global transcriptional profiling; lung adenocarcinoma; malignancy.
© 2017 UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early Loss of Histone H2B Monoubiquitylation Alters Chromatin Accessibility and Activates Key Immune Pathways That Facilitate Progression of Ovarian Cancer.Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 15;79(4):760-772. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2297. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30563893 Free PMC article.
-
let-7b and let-7c microRNAs promote histone H2B ubiquitylation and inhibit cell migration by targeting multiple components of the H2B deubiquitylation machinery.Oncogene. 2017 Oct 19;36(42):5819-5828. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.187. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28604753 Free PMC article.
-
The RING finger domain E3 ubiquitin ligases BRCA1 and the RNF20/RNF40 complex in global loss of the chromatin mark histone H2B monoubiquitination (H2Bub1) in cell line models and primary high-grade serous ovarian cancer.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Dec 15;25(24):5460-5471. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw362. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27798111
-
Histone H2B monoubiquitination: roles to play in human malignancy.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015 Feb;22(1):T19-33. doi: 10.1530/ERC-14-0185. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015. PMID: 24891457 Review.
-
Role of H2B mono-ubiquitination in the initiation and progression of cancer.Bull Cancer. 2021 Apr;108(4):385-398. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2020.12.007. Epub 2021 Mar 6. Bull Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33685627 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Angiogenic Regulators and Anti-Angiogenesis Drugs Targeting Angiogenesis Signaling Pathways: Perspectives for Targeting Angiogenesis in Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 16;12:842960. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.842960. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35372042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cetuximab-Triptolide Conjugate Suppresses the Growth of EGFR-Overexpressing Lung Cancers through Targeting RNA Polymerase II.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020 Jul 6;18:304-316. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.07.001. eCollection 2020 Sep 25. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020. PMID: 32775615 Free PMC article.
-
Writing Histone Monoubiquitination in Human Malignancy-The Role of RING Finger E3 Ubiquitin Ligases.Genes (Basel). 2019 Jan 18;10(1):67. doi: 10.3390/genes10010067. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30669413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Functional Effects of Key Driver KRAS Mutations on Gene Expression in Lung Cancer.Front Genet. 2020 Feb 4;11:17. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00017. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32117436 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the human Bre1 complex bound to the nucleosome.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 22;15(1):2580. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46910-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38519511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Wilting RH, Dannenberg JH. Epigenetic mechanisms in tumorigenesis, tumor cell heterogeneity and drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 2012;15:21–38. - PubMed
-
- Cole AJ, Clifton-Bligh R, Marsh DJ. Histone H2B monoubiquitination: roles to play in human malignancy. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015;22:T19–33. - PubMed
-
- Nicassio F, Corrado N, Vissers JH, et al. Human USP3 is a chromatin modifier required for S phase progression and genome stability. Curr Biol. 2007;17:1972–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

