Histopathological Effects of Bt and TcdA Insecticidal Proteins on the Midgut Epithelium of Western Corn Rootworm Larvae (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera)
- PMID: 28481307
- PMCID: PMC5450704
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins9050156
Histopathological Effects of Bt and TcdA Insecticidal Proteins on the Midgut Epithelium of Western Corn Rootworm Larvae (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera)
Abstract
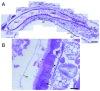
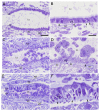
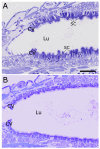
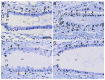
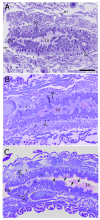
Western corn rootworm (WCR, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte) is a major corn pest in the United States, causing annual losses of over $1 billion. One approach to protect against crop loss by this insect is the use of transgenic corn hybrids expressing one or more crystal (Cry) proteins derived from Bacillus thuringiensis. Cry34Ab1 and Cry35Ab1 together comprise a binary insecticidal toxin with specific activity against WCR. These proteins have been developed as insect resistance traits in commercialized corn hybrids resistant to WCR feeding damage. Cry34/35Ab1 is a pore forming toxin, but the specific effects of Cry34/35Ab1 on WCR cells and tissues have not been well characterized microscopically, and the overall histopathology is poorly understood. Using high-resolution resin-based histopathology methods, the effects of Cry34/35Ab1 as well as Cry3Aa1, Cry6Aa1, and the Photorhabdus toxin complex protein TcdA have been directly visualized and documented. Clear symptoms of intoxication were observed for all insecticidal proteins tested, including swelling and sloughing of enterocytes, constriction of midgut circular muscles, stem cell activation, and obstruction of the midgut lumen. These data demonstrate the effects of these insecticidal proteins on WCR midgut cells, and the collective response of the midgut to intoxication. Taken together, these results advance our understanding of the insect cell biology and pathology of these insecticidal proteins, which should further the field of insect resistance traits and corn rootworm management.
Keywords: Bacillus thuringiensis; Cry34Ab1; Cry35Ab1; Diabrotica virgifera virgifera; histopathology; western corn rootworm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Metcalf R.L. Foreword. In: Krysan J.L., Miller T.A., editors. Methods for the Study of Pest Diabrotica. Springer; New Youk, NY, USA: 1986. pp. vii–xv.
-
- Narva K.E., Siegfried B.D., Storer N.P. Transgenic approaches to western corn rootworm control. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2013;136:135–162. - PubMed
-
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Biopesticides Registration Action Document. Bacillus thuringiensis Cry3Bb1 Protein and the Genetic Material Necessary for Its Production (Vector PV-ZMIR13L) in MON 863 Corn (OECD Unique Identifier: MON-ØØ863-5) [(accessed on 6 May 2017)]; Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/registration/dec....
-
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Biopesticides Registration Action Document. Modified Cry3A Protein and the Genetic Material Necessary for its Production (Via Elements of pZM26) in Event MIR604 Corn SYN-IR604-8. [(accessed on 6 May 2017)]; Available online: http://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/pip/mcry3a-brad.pdf.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

