Effect of Variations in Micropatterns and Surface Modulus on Marine Fouling of Engineering Polymers
- PMID: 28481498
- PMCID: PMC5445506
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b14262
Effect of Variations in Micropatterns and Surface Modulus on Marine Fouling of Engineering Polymers
Abstract
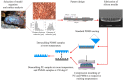
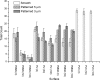
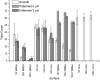
We report on the marine fouling and fouling release effects caused by variations of surface mechanical properties and microtopography of engineering polymers. Polymeric materials were covered with hierarchical micromolded topographical patterns inspired by the shell of the marine decapod crab Myomenippe hardwickii. These micropatterned surfaces were deployed in field static immersion tests. PDMS, polyurethane, and PMMA surfaces with higher elastic modulus and hardness were found to accumulate more fouling and exhibited poor fouling release properties. The results indicate interplay between surface mechanical properties and microtopography on antifouling performance.
Keywords: PDMS; biofouling; poly(methyl methacrylate); polyurethane; surface patterning; surface properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Biomimicking micropatterned surfaces and their effect on marine biofouling.Langmuir. 2014 Aug 5;30(30):9165-75. doi: 10.1021/la502006s. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Langmuir. 2014. PMID: 25017490
-
Modification of Silicone Elastomer Surfaces with Zwitterionic Polymers: Short-Term Fouling Resistance and Triggered Biofouling Release.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Nov 25;7(46):25586-91. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b09199. Epub 2015 Nov 16. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 26554418
-
Mechanical factors favoring release from fouling release coatings.Biofouling. 2000;15(1-3):73-81. doi: 10.1080/08927010009386299. Biofouling. 2000. PMID: 22115293
-
Molecular level studies on interfacial hydration of zwitterionic and other antifouling polymers in situ.Acta Biomater. 2016 Aug;40:6-15. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.02.030. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Acta Biomater. 2016. PMID: 26923530 Review.
-
Effects of surface texture and interrelated properties on marine biofouling: a systematic review.Biofouling. 2019 Jul;35(6):597-617. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2019.1636036. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Biofouling. 2019. PMID: 31298039
Cited by
-
Imparting scalephobicity with rational microtexturing of soft materials.Sci Adv. 2023 Dec 22;9(51):eadj0324. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj0324. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 38117897 Free PMC article.
-
Does plastic type matter? Insights into non-indigenous marine larvae recruitment under controlled conditions.PeerJ. 2022 Dec 19;10:e14549. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14549. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36570004 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of High Aspect Ratio Micro-Structures with Superhydrophobic and Oleophobic Properties by Using Large-Area Roll-to-Plate Nanoimprint Lithography.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jan 29;11(2):339. doi: 10.3390/nano11020339. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33572813 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of surface interactions on the settlement of particles on a sinusoidally corrugated substrate.RSC Adv. 2020 Mar 20;10(19):11348-11356. doi: 10.1039/c9ra10297c. eCollection 2020 Mar 16. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35495333 Free PMC article.
-
Quaternary Ammonium Salts-Based Materials: A Review on Environmental Toxicity, Anti-Fouling Mechanisms and Applications in Marine and Water Treatment Industries.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 7;14(8):957. doi: 10.3390/biom14080957. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199346 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bott T. R.Industrial Biofouling; Elsevier: Kidlington, Oxford, U.K., 2011.
-
- Cooksey K.; Murthy P. S.; Flemming H.-C.; Venkatesan R.. Marine and Industrial Biofouling; Springer: Berlin, 2009.
-
- Thomason J.; Wiley I.; Dürr S.. Biofouling; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, U.K., 2010.
-
- Magin C. M.; Cooper S. P.; Brennan A. B. Non-Toxic Antifouling Strategies. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 36–44. 10.1016/S1369-7021(10)70058-4. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

